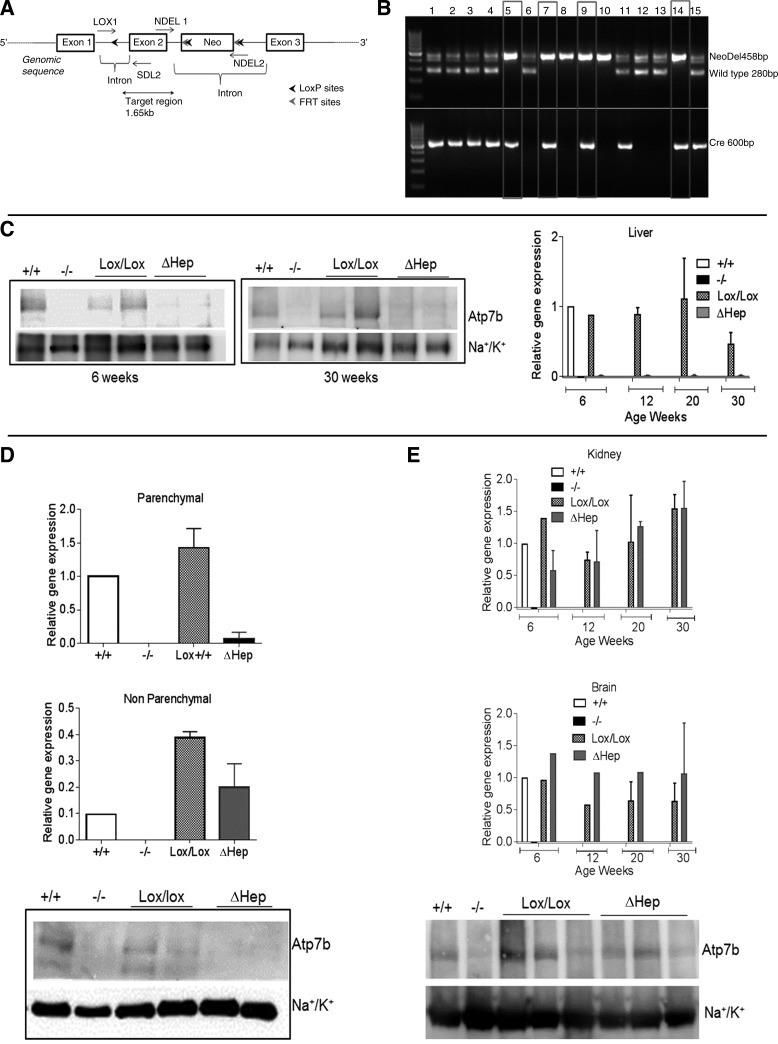
Fig. 1.
Cell-specific inactivation of Atp7b in hepatocytes of Atp7bΔHep mice. A: schematic showing the insertion of loxP sites, the neo cassette, and FRT sites with respect to exon 2 of Atp7b gene. B: verification of genotypes by PCR. The primer set Cre-5 and Cre-3 amplifies a 600-bp region in Alb-Cre-positive animals, and NDEL1 and NDEL2 primers generate a 458 band in animals with Atp7bLox/Lox genotype and 280 band for WT animals; lanes 5, 7, 9, and 14 are consistent with the Atp7bΔHep genotype. C: mRNA levels (right) and representative Western blot (left and middle) for Atp7b in livers of control (Lox/Lox) and Atp7bΔHep (ΔHep) littermates (n = 3–6 for each age and each genotype). Tissues from Atp7b+/+ and Atp7b−/− livers served as additional controls. D: detection of Atp7b mRNA and protein levels in parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells isolated from livers of Atp7bΔHep and Atp7bLox/Lox littermates (n = 2–3). Cells isolated from Atp7b+/+ and Atp7b−/− livers were used as controls. E: Atp7b mRNA levels in the kidneys and the brain at different ages (n = 1–3 for each age and each genotype) and Atp7b protein levels in kidneys.