Fig. 1.
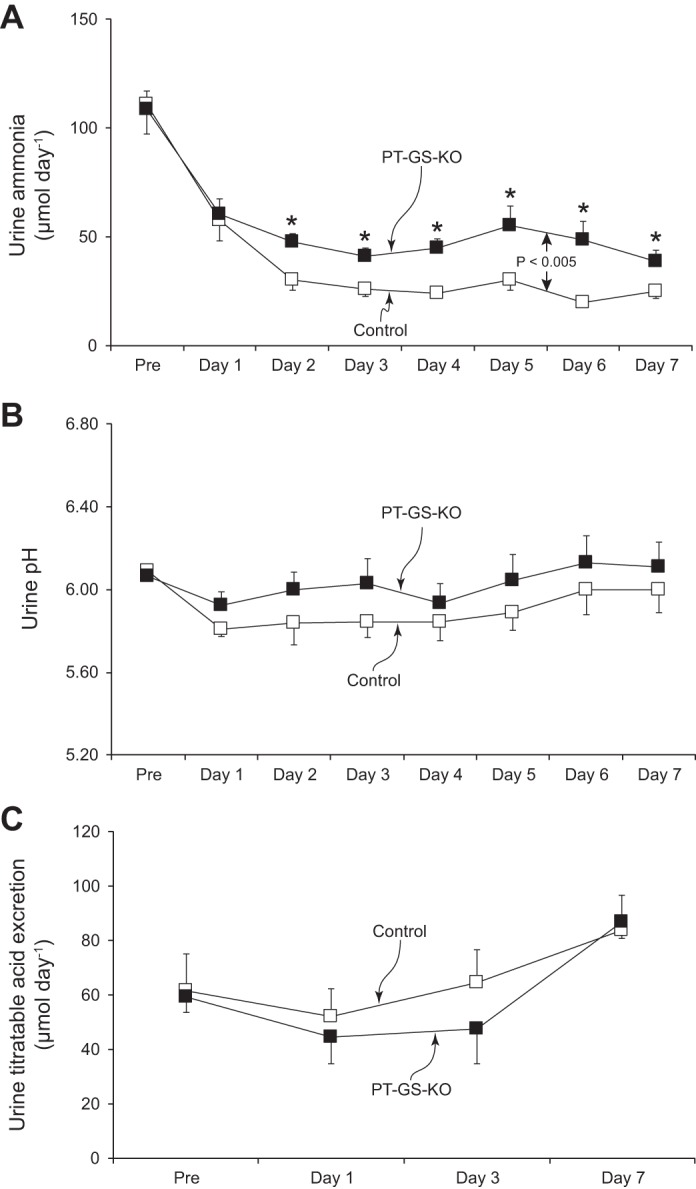
Effect of proximal tubule-specific glutamine synthetase deletion (PT-GS-KO) on urinary ammonia, pH, and titratable acid excretion response to dietary protein restriction. A: changes in urinary ammonia excretion. Initiation of a 6% protein diet caused a rapid decrease in urinary ammonia excretion in both Control and PT-GS-KO genotypes, but the decrease was blunted significantly in PT-GS-KO mice compared with Control mice (P < 0.005). *P < 0.05 vs. Control mice on an individual day; n = 12 mice/genotype. B: changes in urine pH. Urine pH was not different between genotypes and did not change significantly in either genotype during dietary protein restriction; n = 12 mice/genotype. C: titratable acid excretion. There were no time-dependent changes in titratable acid excretion in either genotype during dietary protein restriction and no difference between groups; n = 6 mice/genotype.
