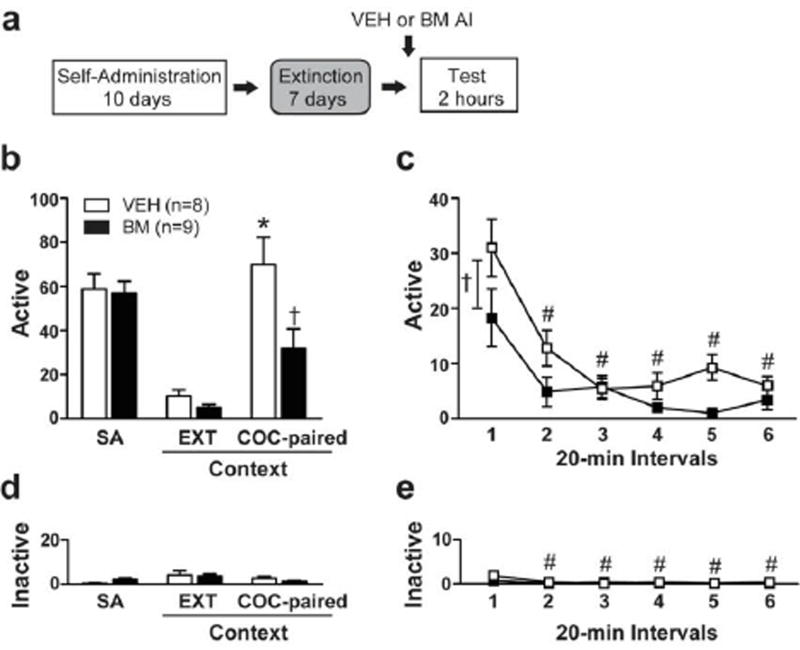
Fig. 2.
AI neural inactivation impairs drug context-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior. (a) Schematic depicting the timeline for Experiment 1. (b) Active and (d) inactive lever responses (mean ± SEM/2 h) during self-administration training (SA, mean of last three sessions), extinction training in the extinction context (EXT, last session), and testing in the cocaine-paired context (COC-paired) for rats that received VEH (white bars/symbols) or BM (1.0mM/0.1 mM; 0.5 µl per hemisphere; black bars/symbols) into the AI immediately before testing. Time course of (c) active and (e) inactive lever responses (mean ± SEM/20 min) at test in the cocaine-paired context. Symbols represent difference relative to the EXT context (* Tukey’s test, P < 0.01), relative to the VEH group († a: Tukey’s test, P < 0.01; b: ANOVA treatment main effect, P = 0.03), or relative to the first 20-min interval (# Tukey’s test, P < 0.01).