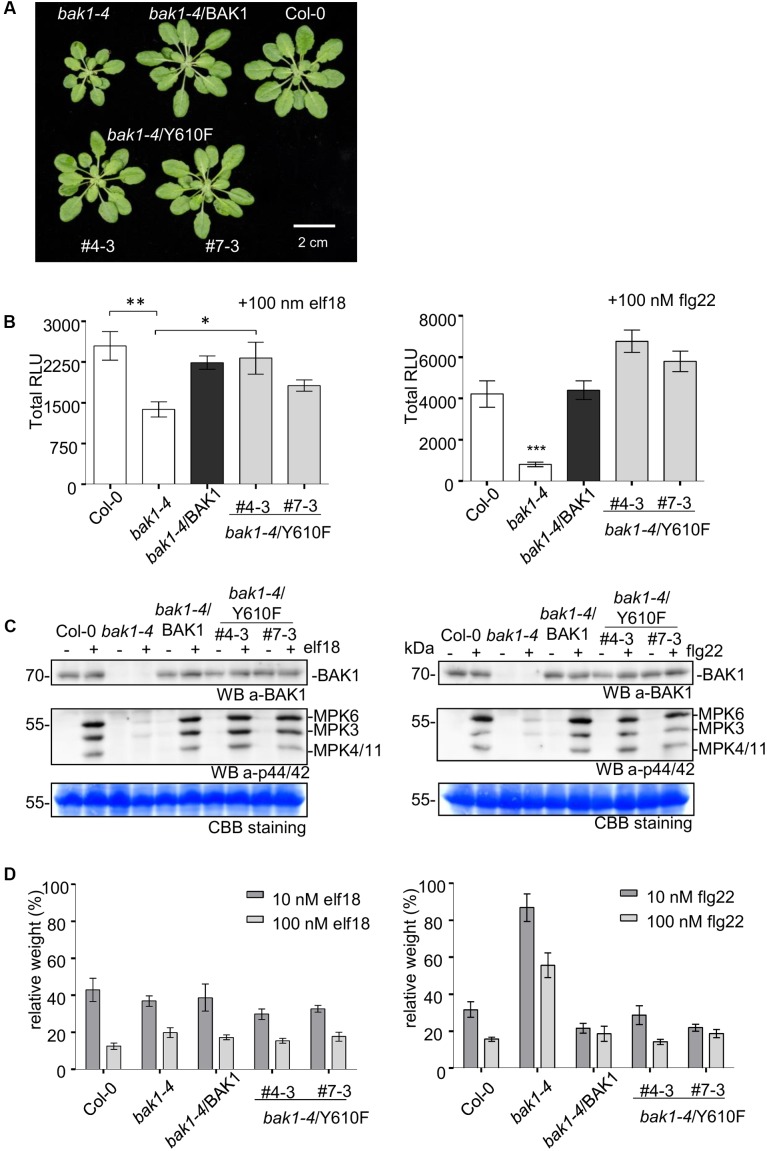
FIGURE 5.
Stable expression of untagged BAK1 or BAK1 (Y610F) rescues the reduced leaf growth phenotype of the bak1-4 mutant but does not affect EFR- and FLS2-dependent PTI signaling. (A) The bak1-4/BAK1 (Y610F) plants have a wild-type-like morphology under short-day conditions. Picture of representative individuals of 35-day-old Col-0, bak1-4, bak1-4/BAK1, bak1-4/BAK1 (Y610F)#4-3, and bak1-4/BAK1 (Y610F)#7-3 plants grown under short-day conditions. Scale bar represents 2 cm. (B) The BAK1 (Y610F) lines display wild-type levels of PAMP-induced ROS in stable Arabidopsis bak1-4 mutant lines. Total ROS production in leaf disks of the indicated genotypes expressed as total relative light units (RLUs) after treatment with 100 nM elf18 (left panel) or 100 nM flg22 (right panel) for 60 min. Values are means ± SE (n = 12). Statistical analysis was performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni post-test (∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05). (C) The BAK1 (Y610F) lines display wild-type levels elf18- (left panel) and flg22-induced (right panel) MAPK activation. Phosphorylation of MAPKs at 5 min after PAMP treatment, as shown by Western Blot using an anti-p44/42-ERK antibody. Individual MPKs are identified by molecular weight and indicated by arrows. The membranes were blotted with anti-BAK1 antibodies and subsequently stained with Coomassie colloidal blue for loading control. (D) BAK1 (Y610F) lines display wild-levels of elf18 (left panel) and flg22 (right panel)-induced seedling growth inhibition. Growth is represented as relative fresh weight to the untreated control. Results are means + SE (n = 8).