Figure 2.
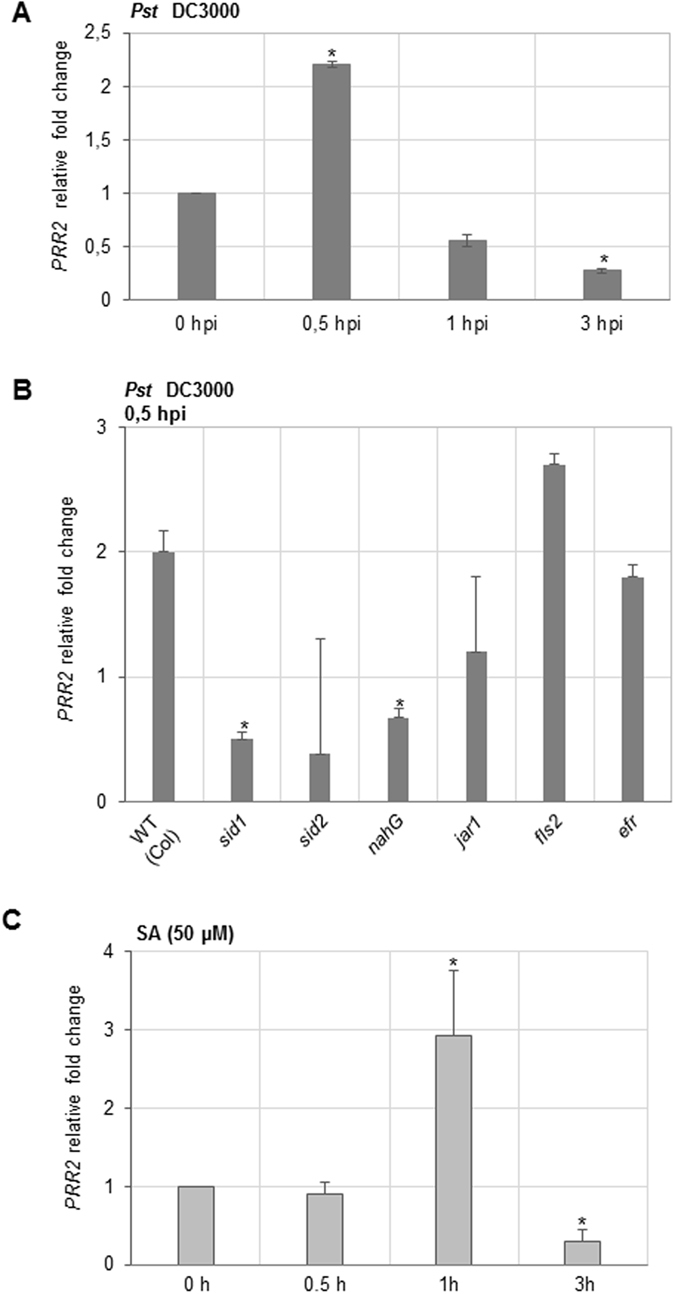
PRR2 gene expression analyses in response to Pseudomonas syringae inoculation and to salicylic acid treatment. (A) PRR2 gene expression in response to P. syringae infection. Leaves of 4-week-old Col plants were inoculated with Pst DC3000 at 5.107 cfu.mL−1. Samples were collected at 0, 0.5, 1 and 3 h post-inoculation (hpi). (B) PRR2 gene expression in mutants defective for hormonal production and MAMP perception. PRR2 expression was monitored 0.5 h after Pst DC3000 inoculation in 4-week-old Arabidopsis mutants defective for SA production (sid1, sid2 and a line carrying the nahG transgene), JA (jar1) signalling pathways but also in mutants altered in flagellin (fls2) or EF-Tu (efr) perception. (C) Time-course of PRR2 gene expression in response to exogenous application of salicylic acid (SA 50 µM). Seedlings were collected at 0, 0.5, 1 and 3 h after SA treatment. All the expression analyses are presented as a fold change relative to mock treatment. Relative transcript quantification was assayed by quantitative real-time PCR and calculated by the comparative 2−ΔΔCT method using actin8 as a reference gene. Data illustrated represent the mean ± SE of three biological replicates from two independent experiments. Asterisks (*) above histograms (ANOVA, p-value 0.05) indicate significant changes of PRR2 gene expression in these different genetic backgrounds compared to WT (Col).
