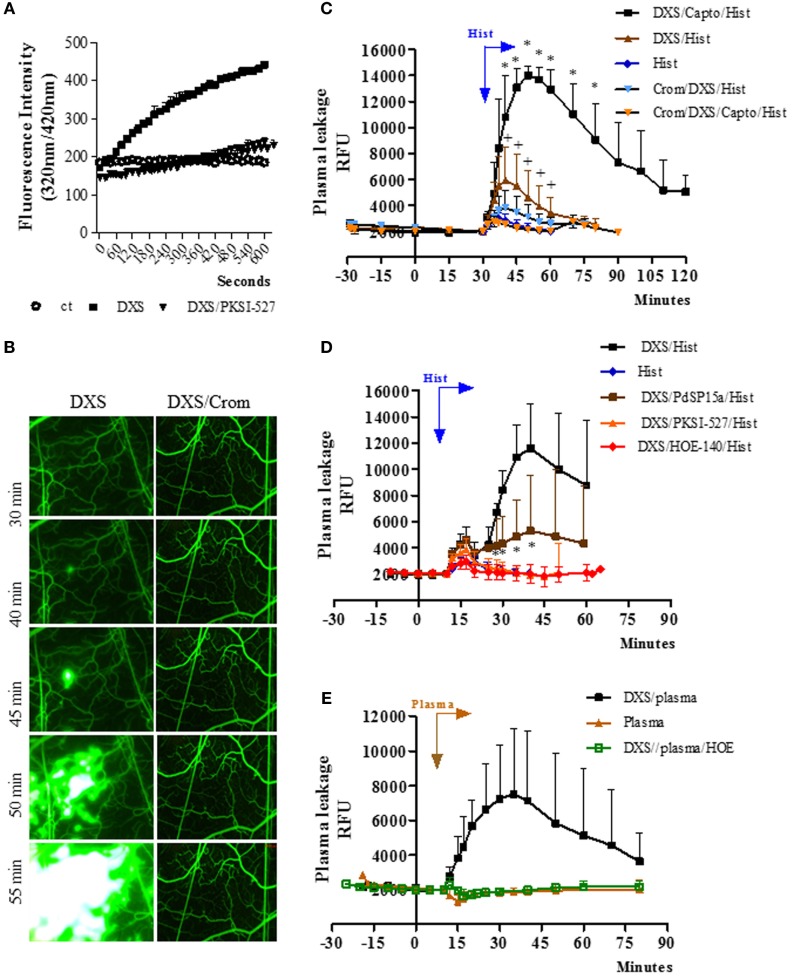
Figure 1.
Bradykinin-induced microvascular leakage is propagated via coupling of mast cell and contact phase factors. (A) Enzyme assays performed with high molecular weight kininogen mimetic substrate detect plasma kallikrein (PKa) activity in fresh hamster plasma (citrated) incubated with the contact activator dextran sulfate (DXS) (20 nM). The kinetics of hydrolysis was performed in the presence/absence of the PKa inhibitor PKSI-527. Substrate hydrolysis was monitored by the increase of fluorescence with time (mean ± SD). Data are representative of three independent experiments run in duplicates. (B–E) Microvascular leakage in the hamster cheek pouch (HCP) sensitized with DXS. (B) HCPs were superfused with DXS (4 µM) for 45 min and fluorescence was visualized at different time-points (representative images, n = 6). Where indicated, the hamsters were pretreated with cromoglycate. (C) Synergism between histamine and DXS was studied after 30 min tissue superfusion, with medium supplemented with DXS 0.4 µM, in the presence or absence of captopril, followed by 5 min of histamine application, i.e., without any interruption of superfusion., DXS/Hist (n = 5), DXS/Capto/Hist (n = 5). Where indicated, the hamsters were pretreated i.p. with cromoglycate (n = 2, and n = 4, in the presence and absence of captopril, respectively). Histamine-induced leakage (n = 12) was inserted (internal controls) for comparison. (D) Evidence that synergism between DXS/histamine leads to leakage via activation of the kallikrein–kinin system was sought in HCP superfused for 10 min with DXS (2 µM) and captopril, followed by 5 min of superfusion with DXS/histamine application (n = 9). Prior to the application of histamine, the DXS-treated HCPs were either treated (superfusion interrupted) with the contact phase inhibitor PdSP15a (n = 6) or with PKa inhibitor PKSI-527 (n = 5) for 5 min. HOE-140 (n = 4), the B2R antagonist (B2RA) was applied together with DXS + Captopril. (E) For plasma reconstitution experiments, HCPs were superfused with DXS + Captopril for 10 min, followed by topical application (superfusion interrupted) of heparinized hamster plasma for 7 min. Plasma (n = 5), and DXS/plasma (n = 8). HOE-140 (n = 4) was applied along with DXS + Captopril before addition of plasma. Data are expressed as: (C–E) Relative fluorescence units (RFUs) (mean ± SD). Statistical analyzes were done by analysis of variance and t-test. In (C), *P < 0.05 DXS/Capto/Hist versus DXS/Hist and +P < 0.05 for DXS/Hist versus DXS/Crom/Hist and D, *P < 0.05 DXS/PdSP15a/Hist versus DXS/Hist.