Figure 1.
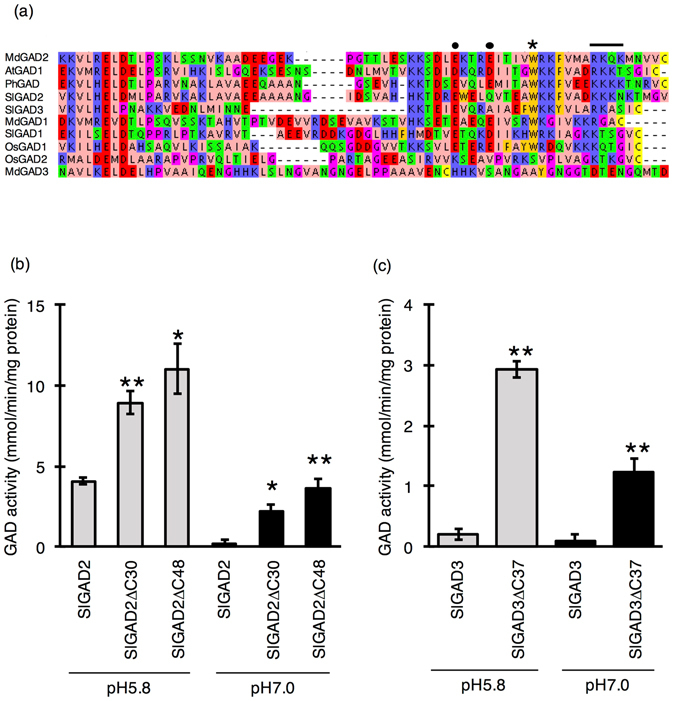
Determination of the target sites within SlGADs’ C-terminal regions. (a) Multiple sequence alignment of the C-terminal region of 10 plant GADs. The C-terminal of MdGAD1-3, AtGAD1, PhGAD, OsGAD1-2, SlGAD1-3 from Malus domestica (apple), Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa (rice), and Solanum lycopersicum (tomato), respectively, which were obtained in a previous study, were compared. The conserved tryptophan (W) residue and lysine (K) clusters involved in CaM-binding19, 48 are indicated by an asterisk and a black line, respectively. The two glutamate (E) residues functioned as pseudo-substrates and are likely involved in autoinhibition in PhGAD43 are indicated as black circle. Accession Numbers: MdGAD1, KC812242; MdGAD2, KC812243; MdGAD3, KC812244; AtGAD1, AY094464.1; AtGAD2, U49937.1; PhGAD, L16977; SlGAD1, AB359913; SlGAD2, AV359914.1; SlGAD3, AB359915.1; OsGAD1, AB056060; OsGAD2; AB056061. (b and c) GAD activity of SlGAD2ΔC30 and SlGAD2ΔC48, and SlGAD3Δ37, respectively, in in vitro assays. Crude extracts from Escherichia coli were used in GAD enzymatic assays and Ca2+ was not included in reaction buffers. SlGAD2 and SlGAD3 are full-length GADs, whereas SlGAD2ΔC30, SlGAD2ΔC48, and SlGAD3ΔC37 are truncated GADs at C-terminal positions 30, 48, and 37, respectively. Bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3) and asterisks indicate statistical differences in according to the Tukey-Kramer’s test between full-length GADs (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).
