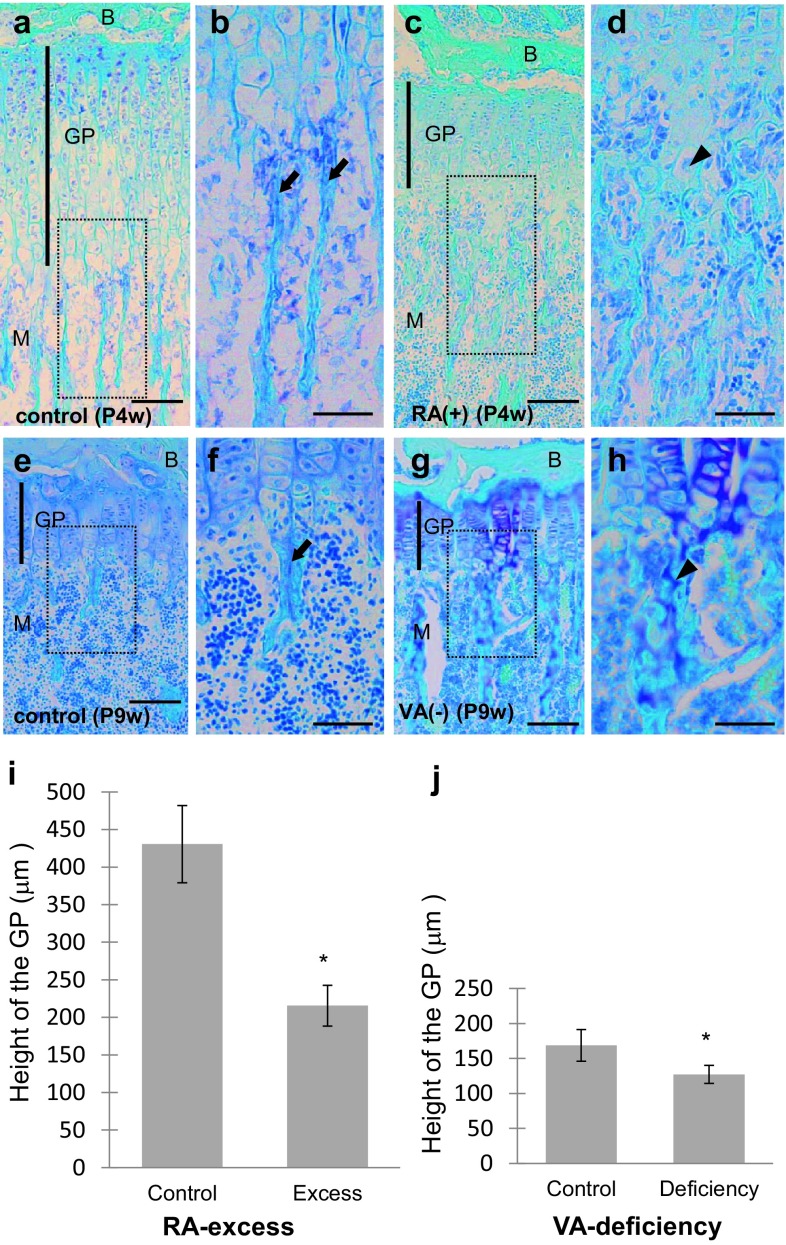
Fig. 1.
The growth plate (GP) in mouse tibiae. Light micrographs of toluidine blue-stained sections at lower (a, c, e, g) and higher (b, d, f, h squares in a, c, e, and g, respectively) magnifications and graphs (i, j) showing the effects of retinoic acid (RA)-excessive administration for 4-week-old (P4w) (c, d; a, b: control) or vitamin A (VA)-deficient diet (g, h, 6 weeks from P3w; e, f: control) on the GP of the proximal tibiae of mice. B epiphyseal bone, M metaphysis, arrows trabeculae, arrowheads cartilage, scale bars 100 μm; mean ± SD; *P < 0.01 (n = 50)