Figure 1.
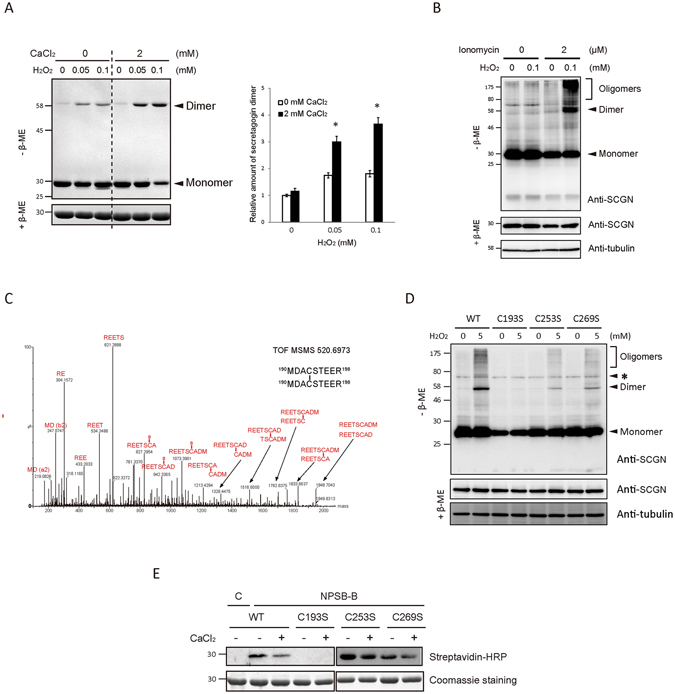
Calcium binding of hSCGN promotes H2O2 induced dimerization via C193-C193 disulfide linkage. (A) Recombinant hSCGN was incubated with 0 or 2 mM CaCl2 at R.T. for 15 min followed by H2O2 treatment in indicated concentration at 37°C for 1 h. Proteins were detected with coomassie blue-staining (left panel) and dimer formations were quantified and normalized with reduced form of SCGN (right panel). Data are presented as mean ± SD of three experiments (*P < 0.05, Student’s t-test). (B) NIT-1 insulinoma cells overexpressing hSCGN WT were pre-incubated with 0 or 2 μM ionomycin for 5 min followed by incubation with 0 or 100 μM H2O2 for 30 min at 37 °C. Total protein lysates were analyzed by Western blots using anti-SCGN or anti-α-tubulin antibody. (C) Tandem mass spectrum of C193-C193 disulfide linked peptide in band #7 and 8 of Supplementary Fig. S2A. (D) HeLa cells overexpressing SCGN WT, and Cys mutant (C193S, C253S, C269S) were treated with 0, 5 mM H2O2 for 10 min at 37°C. The total lysates were separated on non-reducing and reducing SDS PAGE and hSCGN and tubulin were detected by Western analysis. Tubulin was used for loading control. Non-specific bands were indicated as *. (E) hSCGN WT, and Cys mutants were incubated with 2 mM CaCl2 at R.T. for 15 min followed by treatment with 1 mM NPSB-B at R.T. for 2 h. Proteins were separated on reducing SDS-PAGE and detected by streptavidin-HRP. Coomassie staining gel showing amount of gel loaded proteins. Full-length gels and blots are in Supplementary Fig. S6.
