Figure 1.
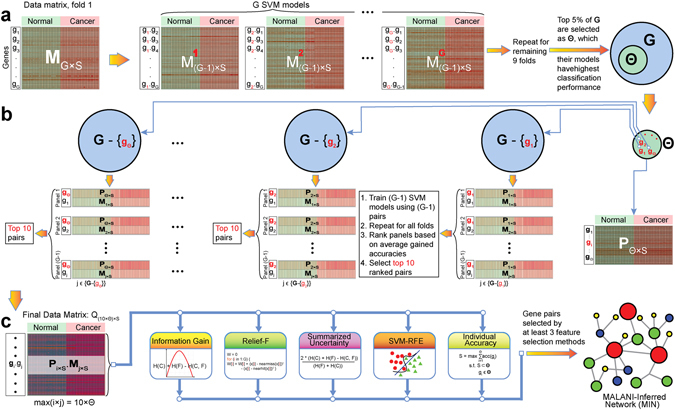
Overview of Machine Learning-Assisted Network Inference (MALANI) algorithm to infer a cancer network for a given cancer type. The overall MALANI procedure consists of three major stages: (a) Stage 1: Construction of gene-wise models. Step 1.1: Split gene expression data matrix for 10-fold cross-validation. Original gene expression matrix is represented as M G×S where G represents the number of genes (rows in data matrix) and S represents samples (column in data matrix). The gene expression matrix was split into 10 portions, each for cancer and normal samples. Step 1.2: Construct gene-wise dot product matrices. For the first training fold, gene-wise dot product matrices are constructed from split data from step 1.1. Step 1.3: Model training and testing. Gene-wise matrices generated from Step 1.2 were used for training and the remaining one split portion as testing. The step was then repeated 9 times for 10-fold cross-validation (see Materials and Methods for more detailed description). Step 1.4: Evaluation of gene-wise model performance. Performance of gene-wise dot product models were assessed for their capability to classify cancer vs. normal samples. The top 5% gene-wise models with the best classification performance that constitute a gene set of Θ were selected. (b) Stage 2: Construction of gene-pair models. Step 2.1: Construction of gene-pair vector from Θ set. Using data from Step 1.1, vectors of gene pairs from a set of Θ genes obtained from Step 1.4 (denoted as red “g”) with remaining genes in the expression array (denoted as black “g”) were constructed. Step 2.2: Model training and testing. Each vector corresponding to a gene in set Θ were used to train SVM models for each training fold and 10-fold cross-validation procedure as described in Step 1.3 was performed. Step 2.3: Evaluation of gene-pair model performances. Gene-pair model performance was assessed based on model’s capability to classify cancer vs. normal samples. Genes not found in the Θ set (black “g”) that paired with genes in the Θ set (red “g”) and were among the top 10 in terms of best classification performance were deemed functionally associated with a given gene in set Θ. (c) Stage 3: Inferring cancer networks. Step 3.1: Construction of finalized gene-pair dot product matrix. Step 3.2: Assessment of gene pair performance in classifying cancer samples. Five feature selection methods were used to assess performance of each gene pair dot product in classifying cancer vs. normal samples. Step 3.3: Construction of MALANI-Inferred Network (MIN) for a cancer. Selected gene pairs by at least three different feature selection methods in Step 3.2 were then agglomerated to reconstruct an inferred cancer network.
