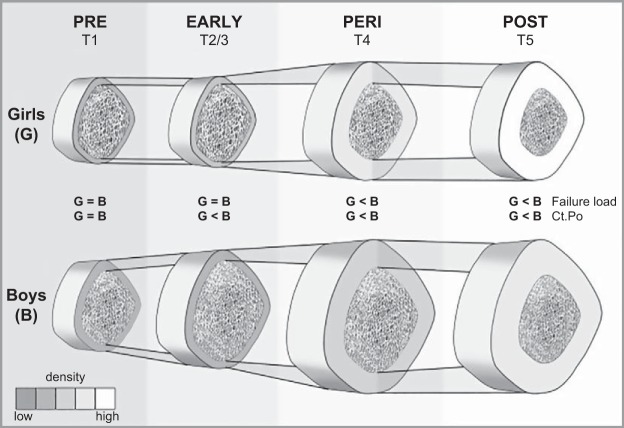
FIGURE 7.
Schematic representation of the differences in cortical bone structure and density for girls (G) and boys (B) across puberty [by Tanner (T) stage]. Boys acquire higher estimated bone strength (failure load) due to their greater cortical bone diameter. The medullary cavity is also wider in boys, resulting in only mildly greater cortical thickness. Volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD) is higher in girls (whither cortex). Trabecular bone volume and cortical porosity (Ct.Po) are also higher in boys (differences not depicted). [From Nishiyama et al. (375), with permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.]