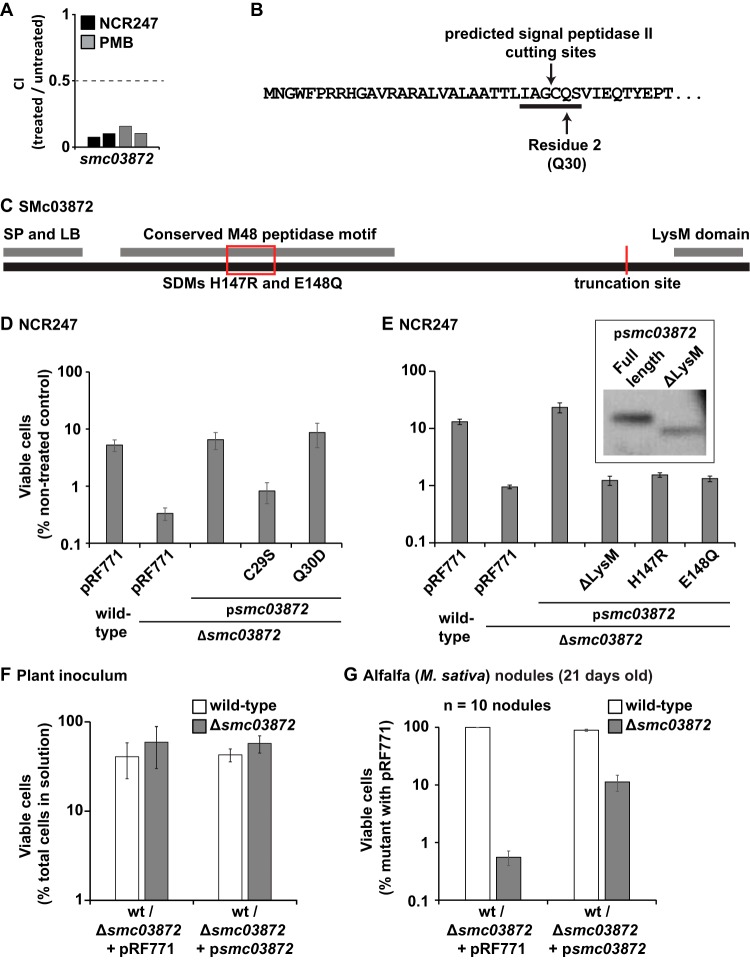
FIG 5 .
The putative S. meliloti metallopeptidase protects against NCR247 and provides a competitive disadvantage. (A) Tn-seq results for gene smc03872 showing both replicates for NCR247 and PMB. (B) N-terminal amino acid sequence of the SMc03872 protein highlighting the conserved lipobox and predicted signal peptidase cutting site. (C) Schematic representation of SMc03872 highlighting the predicted N-terminal signal peptide (SP) with the conserved lipobox (LB), the conserved metallopeptidase domain, and the conserved C-terminal LysM domain. The approximate locations of the two introduced site-directed mutations and the truncation site are indicated in red. (D and E) Early-log-phase cells of the indicated wild-type and mutant S. meliloti strains were treated with two doses of 6 µM NCR247-AR over a time course of 24 h. (F) Bacterial composition of alfalfa plant inoculum of the indicated strains. Values are means ± standard deviations (error bars). wt, wild type. (G) Bacterial cells recovered from 21-day-old nodules represented by the fraction of bacteria recovered with a peptidase mutant with and without a complementation construct. Values are means ± standard errors (error bars) for 10 nodules. All experimental results shown are representative for trends observed in at least two independent experiments.