Figure 2.
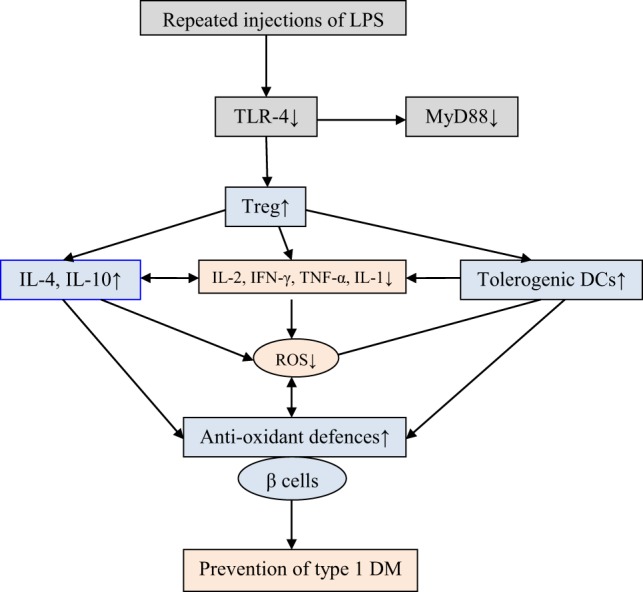
Multiple-injections of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is effective in preventing type 1 diabetes mellitus (type 1 DM). LPS administration suppresses spleen T lymphocyte proliferation, increases the generation of T regulatory, reduces the synthesis of T-helper 1 pro-inflammatory cytokines [interleukin-2 (IL-2), interleukin-1 (IL-1), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)], and downregulates toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4) and its downstream MyD88-dependent signaling pathway and enhances IL-4 and IL-10 and antioxidant defenses. Multiple injections of LPS induce tolerogenic dendritic cell (DC) subset with low TLR-4 expression and, thus, prevent development of type 1 DM in non-obese diabetic mice [see text and Wang et al. (47)].
