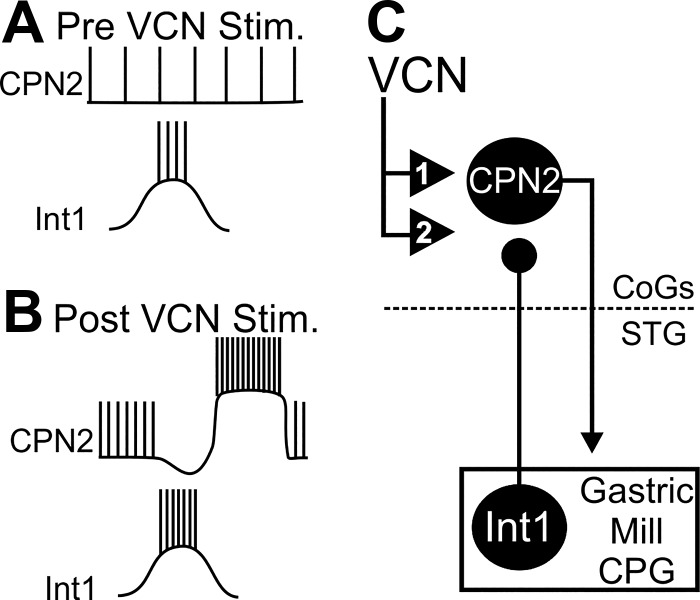
Fig. 10.
Summary of the VCN modulatory actions on CPN2 and Int1 feedback. A: in control conditions, CPN2 is weakly active and is not inhibited by Int1. B–C: modulatory VCN actions trigger a long-lasting increased CPN2 firing rate relative to control (1) (Beenhakker and Nusbaum 2004; Blitz and Nusbaum 2007a). Additionally, after VCN stimulation, the Int1 inhibition of CPN2 is strengthened (2). The enhanced Int1 inhibition of CPN2 triggers postinhibitory rebound in CPN2, which increases CPN2 intraburst firing rate above that due to VCN modulatory actions on CPN2. Ball and stick represent an inhibitory synapse. Numbered triangles indicate modulatory actions.