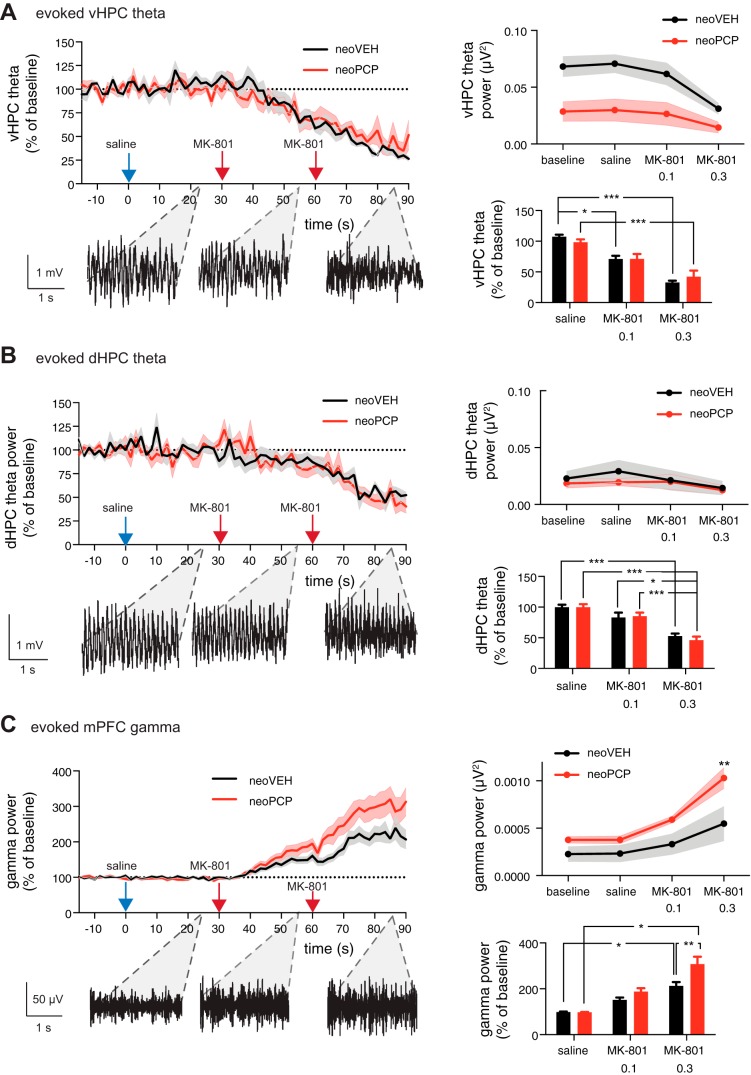
Fig. 3.
Rats administered PCP neonatally display hypersensitive gamma oscillations in response to acute MK-801 application. A: animals were administered saline sc and then injected sc with 0.1 mg/kg and 0.2 mg/kg MK-801 at 30 and 60 min after the saline injection, respectively, while local field potentials in ventral hippocampus (vHPC), dorsal hippocampus (dHPC), and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) were recorded. MK-801 application reduced vHPC theta power (unpaired t-test, P < 0.001), with no difference between the relative reductions in neoVEH and neoPCP animals. The evoked absolute theta power baseline before MK-801 application was decreased in neoPCP compared with neoVEH rats (unpaired t-test, P = 0.0104; Holm-Sidak multiple-comparison post hoc test, P < 0.001). B: MK-801 administration reduced evoked normalized theta power in dHPC (unpaired t-test, P < 0.0001), with no difference between the baseline theta level and the relative size of the reduction between neoVEH and neoPCP rats. C: MK-801 increased gamma power in neoPCP animals (unpaired t-test, P < 0.0001; Holm-Sidak multiple-comparison post hoc test, P < 0.0001) to a greater extent than in control animals (Holm-Sidak multiple-comparison post hoc test, P = 0.0043). Data are represented as means ± SE. vHPC: neoVEH, n = 5; neoPCP, n = 7. dHPC: neoVEH, n = 9; neoPCP, n = 10. mPFC: neoVEH, n = 11; neoPCP, n = 14. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.