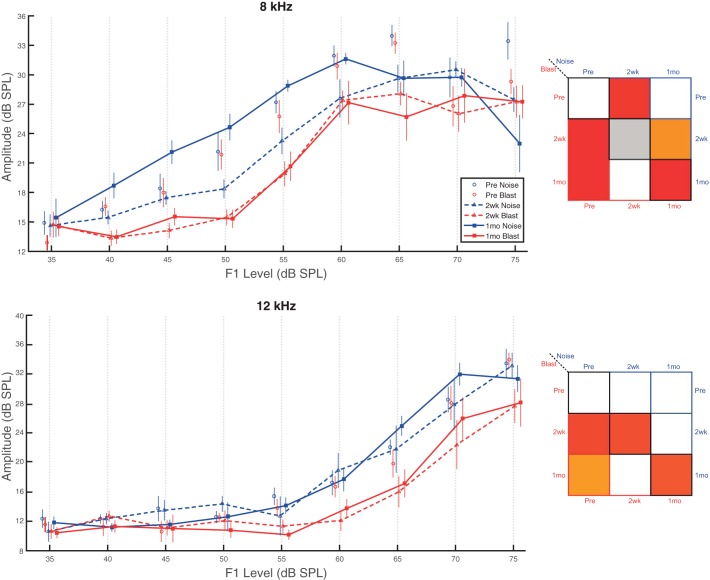
Fig. 3.
Blast animals demonstrated more severe and persistent deficits on higher frequency DPOAEs. DPOAEs at 8 and 12 kHz revealed group- and time point-dependent I/O function differences. Top, pure tones set at 8 kHz. Both blast and noise animals demonstrated significant differences at 2 wk postinjury from preinjury recordings. At 1 mo postinjury, only blast group recordings were significantly lower (worse) than preinjury, at which point between-group differences also emerged. Bottom, pure tones set at 12 kHz. Only blast group animals demonstrated significant reductions (worse) compared with preinjury recordings at both the 2-wk and 1-mo postinjury time points. Between-group differences were also present at both 2 wk and 1 mo with blast group results lower (worse) than the noise group. Data are means ± SE.