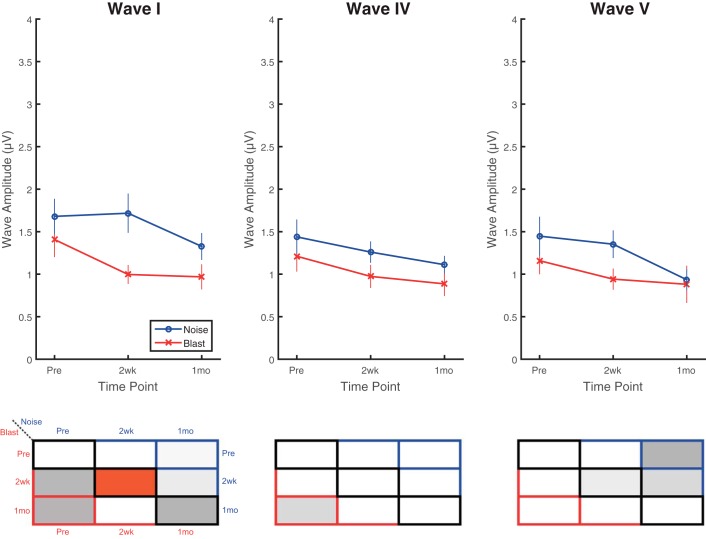
Fig. 8.
Deficits observed on tone-burst ABRs were less apparent than on click ABRs. Significant differences were observed using 80-dB pSPL, 8-kHz tone-burst ABRs between blast and noise groups at 2 wk postinjury with similar overall trends to click ABR results. Blast animals demonstrated trends of decrease (worse) in 2-wk postinjury wave I (top), IV (middle), and V (bottom) amplitudes that appeared to flatten and sustain to 1 mo postinjury, but changes were not significant compared with preinjury results. Trends in wave amplitude decreases (worse) in noise animals that occurred between 2 wk and 1 mo postinjury were also nonsignificant. Wave I amplitudes captured the only significant difference between blast and noise groups at 2 wk postinjury. Data are means ± SE.