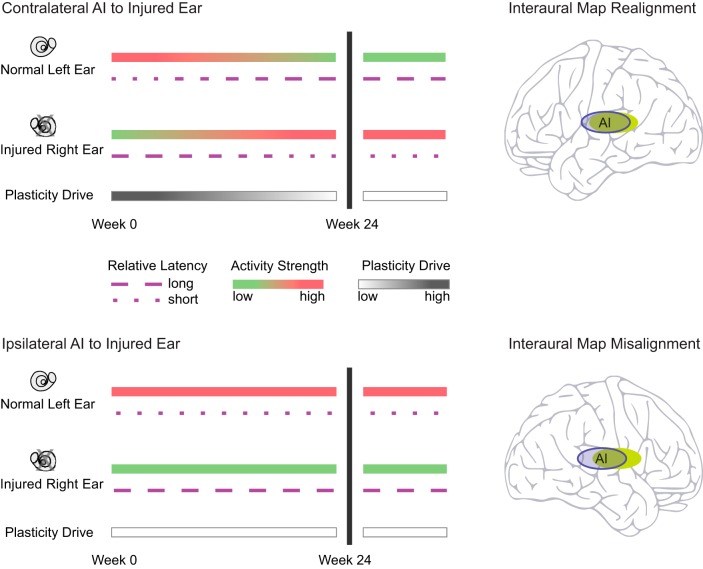
Fig. 9.
Summary of factors that drive cortical reorganization in mild-to-moderate asymmetric hearing loss. Top: contralateral AI is driven to plastic change, despite relatively low activity strength of the injured right ear secondary to higher thresholds. The key factor driving cortical reorganization is abnormal interaural latency. By week 24, interaural frequency maps come into realignment, interaural latency difference is restored to the normal value, and plasticity drive becomes low. Bottom: ipsilateral AI is in a low plasticity drive state as the normal left ear has relatively lower thresholds after acoustic injury to the right ear and normal interaural latency is not perturbed. By week 24, interaural frequency maps persist in misalignment. Anisomorphic cortical reorganization in mild-to-moderate asymmetric SNHL has stabilized.