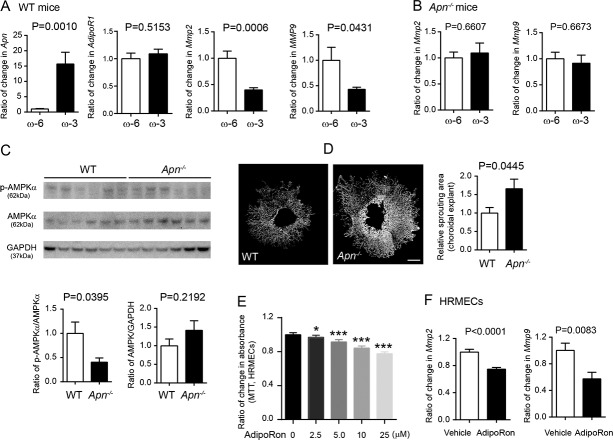
Figure 3.
The APN pathway inhibited neovessel formation through the suppression of MMP expression in laser-induced CNV. (A) WT mice fed ω-3 versus ω-6 LCPUFA-enriched diets had increased Apn, and decreased Mmp2 and Mmp9, as well as unchanged AdipoR1 expression in choroidal-retinal explants. n = 3 mice per group. Unpaired t-test. (B) APN deficiency abolished ω-3 LCPUFA inhibition of choroidal-retinal Mmp2 and Mmp9 levels. n = 3 to 4 mice per group. Unpaired t-test. (C) APN deficiency decreased the levels of phosphorylated AMPKα in choroidal-retinal CNV explants. n = 6 mice per group. Unpaired t-test. (D) In the choroidal sprouting assay ex vivo, choroidal explants from Apn−/− mice showed larger sprouting areas than WT mice. n = 4 to 6 explants per group. Unpaired t-test. Scale bar: 500 μm. (E) In HRMEC MTT assay in vitro, activation of the APN pathway with APN receptor agonist adipoRon inhibited endothelial cell proliferation. n = 10 replicates per group. Unpaired t-test. (F) AdipoRon treatment (25 μM) decreased Mmp2 and Mmp9 expression in HRMECs. Results were repeated in two independent experiments. Unpaired t-test.