Figure 5.
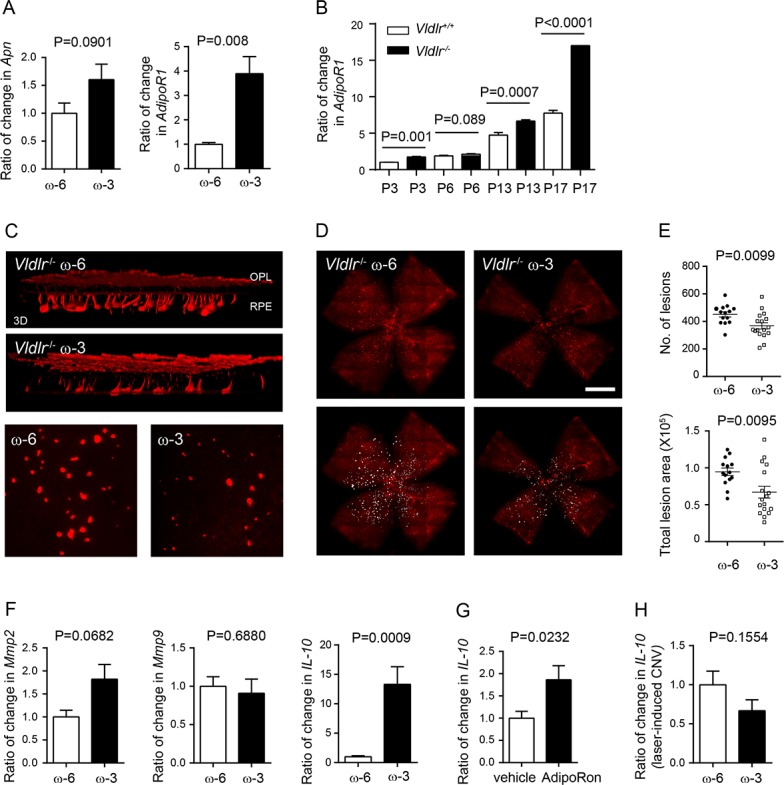
Dietary ω-3 LCPUFA decreased retinal neovascular lesions in Vldlr−/− mice. Vldlr−/− mice were fed either ω-3 or ω-6 LCPUFA-enriched diets from postnatal day (P) P1. (A) In Vldlr−/− retinas, ω-3 LCPUFA induced gene expression of APN receptor adipoR1 but not Apn (n = 3 to 4 mice per group). Unpaired t-test. (B) Increased AdipoR1 mRNA levels in Vldlr−/− versus Vldlr+/+ retinas from postnatal day 3 to 17. Unpaired t-test. (C) At P16, retinal neovascularization was examined. 3D reconstruction demonstrated blood vessels invading from the OPL toward RPE; representative images of neovascular lesion (200× magnification). (D) Representative images of isolectin-stained vessels (red) in retinal whole mounts. (E) Dietary ω-3 versus ω-6 LCPUFA supplementation decreased the number and total lesion area of neovascular lesions (n = 7 to 10 mice per group). Unpaired t-test. (F) ω-3 versus ω-6 LCPUFA did not affect retinal Mmp2 and Mmp9 expression in Vldlr−/− mice. Retinal IL-10 was increased in ω-3 LCPUFA-fed Vldlr−/− mice. n = 3 to 4 mice per group. Unpaired t-test. (G) Change in IL-10 in Vldlr−/− mice treated with either 50 mg/kg adipoRon or vehicle from P3 to 15. n = 3 to 4 retinas per group. (H) In the model of laser-induced CNV, there was no change in IL-10 expression in choroidal-retinal complex from WT mice fed ω-3 versus ω-6 LCPUFA-enriched diets. n = 3 mice per group. Unpaired t-test.
