Figure 1.
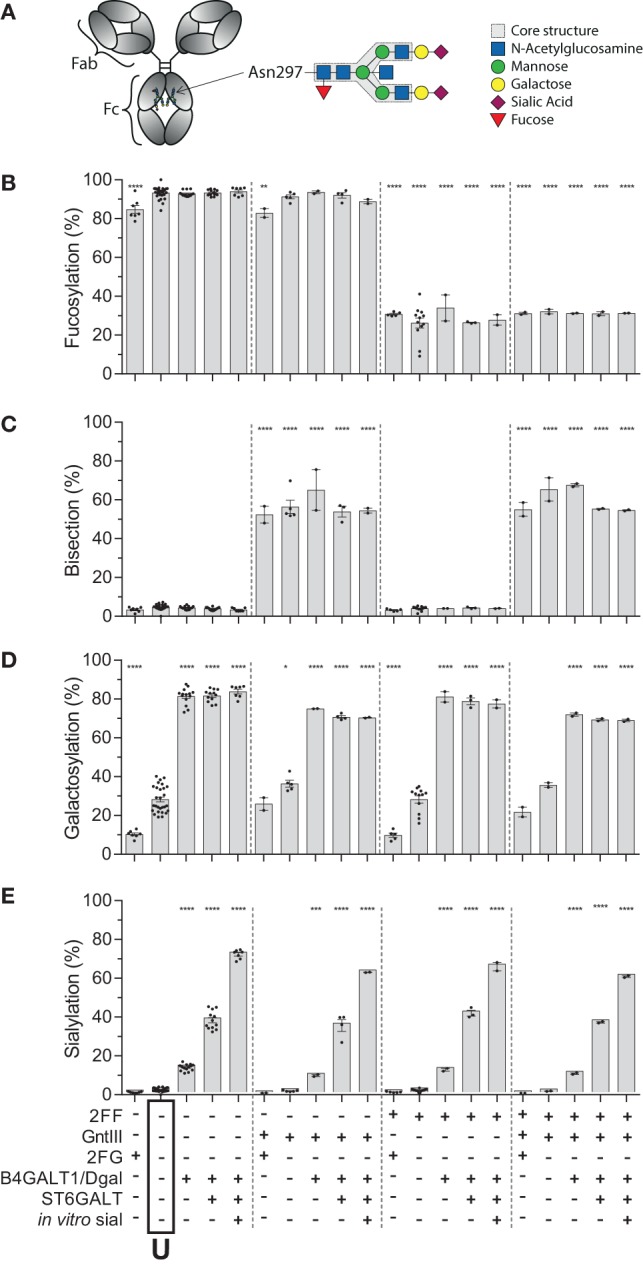
Recapitulation of 20 different immunoglobulin G (IgG) glycoforms by glyco-engineering. (A) Model of IgG with glycan at position N297 in the Fc domain and composition of the glycan. (B–E) Degree of derived glycan traits as reached by the different glyco-engineering tools: 2FF, 0.4 mM 2-deoxy-fluoro-l-fucose; GntIII, 1% GntIII co-transfection; 2FG, 1 mM 2-deoxy-fluoro-d-galactose; B4galT1/Dgal, 1% B4GALT1 co-transfection and 5 mM d-galactose; ST6GALT, 2.5% ST6GALT co-transfection, in vitro sial, treatment of IgG with recombinant ST6GALT and CMP-NANA substrate. The data represent the mean and SEM of at least two combined independent experiments; *, **, ***, and **** denote a statistical significance of p ≤ 0.05, p ≤ 0.01, p ≤ 0.001, and p ≤ 0.0001, respectively, as tested by one-way ANOVA against unmodified IgG1, using Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. U: unmodified glycoform.
