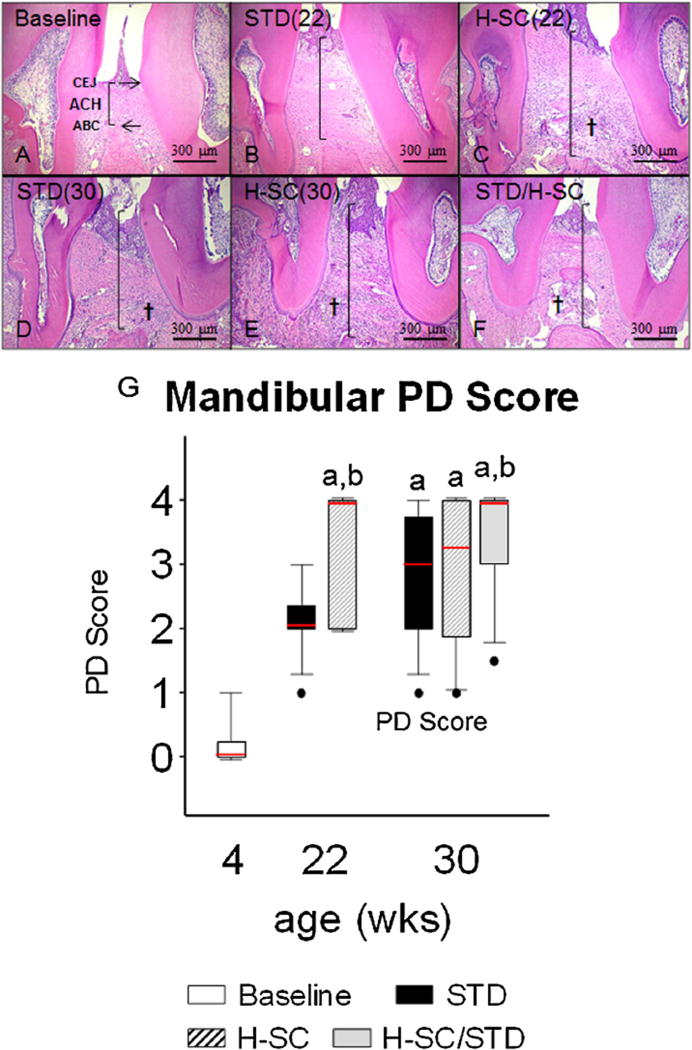
Fig. 6.
Alveolar Crest Height and Periodontitis (PD) Score in representative animals from groups aged 30 weeks or less. Photomicrographs of histologic sections from the interdental region between the first and second mandibular molars of rats from groups: Baseline (A), age 22 weeks with standard diet [STD (22)] (B); age 22 weeks with H-SC diet [H-SC(22)](C); age 30 weeks with STD diet [STD (30)] (D); age 30 weeks with H-SC diet [H-SC (30)] (E); and age 30 weeks after H-SC diet for 18 weeks, then STD diet for 8 weeks (H-SC/STD) (F). Note worse alveolar crest height (ACH) at ages 22 and 30 weeks (B–F) than at Baseline (A). Also note that whereas the inflammatory reaction in periodontal tissues (†) is more pronounced and ACH is worse in H-SC than in STD rats at age 22 weeks (C vs B), the STD and H-SC diets have comparable inflammation and ACH (D vs. E) by age 30 weeks. In (A), note CEJ and ABC. Vertical black lines demonstrate ACH. † Inflammatory cell infiltration of the lamina propria and periodontal ligament (PDL). Scale Bars = 300 µm. Mandibular PD Score (G). Box-whisker plot data represent Mean ± SEM. a: different from Baseline; b: different from STD (22) (P < 0.05).