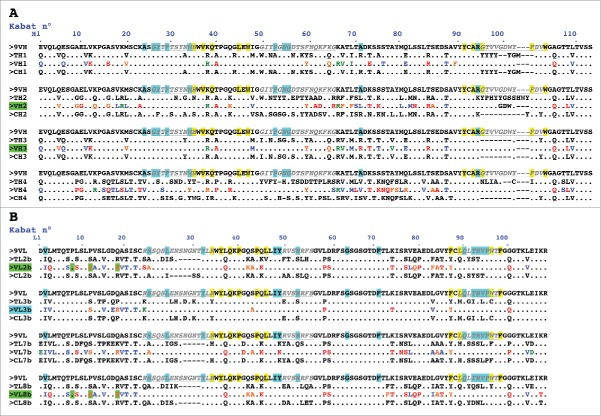
Figure 1.
Design of humanized 9O12 V-domains. (A) Sequence alignment of the mouse 9O12 IGHV (9VH) (most similar human germline sequence being IGHV1–3*01) with 4 human or humanized IGHV templates (TH1: IGHV1–3*01; TH2: bevacizumab; TH3: IGHV1–46*01; TH4: NEW), the humanized 9O12 IGHV variants (VH1, VH2, VH3 and VH4) and the framework regions of their most similar human germline genes (CH1: IGHV1–3*01; CH2: IGHV3–23*04; CH3: IGHV1–46*01; CH4: IGHV4–38–2*02). The humanized variants that retained antigen-binding activity are highlighted in green. (B) Sequence alignment of the mouse 9O12 IGKV (9VL) (most similar human germline sequence being IGKV2–29*02) with 4 human or humanized IGKappaV templates (TL2b: bevacizumab; TL3b: IGKV2–29*02; TL7b: canakinumab; TL8b: REI), the humanized 9O12 IGKV (variants VL2b, VL3b, VL7b and VL8b) and the framework regions of their most similar human germline genes (CL2b: IGKV1–39*01; CL3b: IGKV2–29*02; CL7b: IGKV6–21*01; CL8b: IGKV1–33*01). The humanized variants that retained antigen-binding activity and acquired PpL recognition site are highlighted in green (or in blue if retaining antigen binding activity but not PpL recognition). CDRs are in italic, underlined, gray. Residues at key sites28,49 for canonical structures are highlighted in blue. Residues buried in VH/VL interfaces are underlined in yellow. Residues critical for PpL binding are highlighted in green. Based on the physico-chemical classes of the amino acids (AA), differences in the framework regions of mouse 9O12 and its humanized variants are classified into very similar AA (green), similar AA (blue), dissimilar AA (orange) and very dissimilar AA (red).