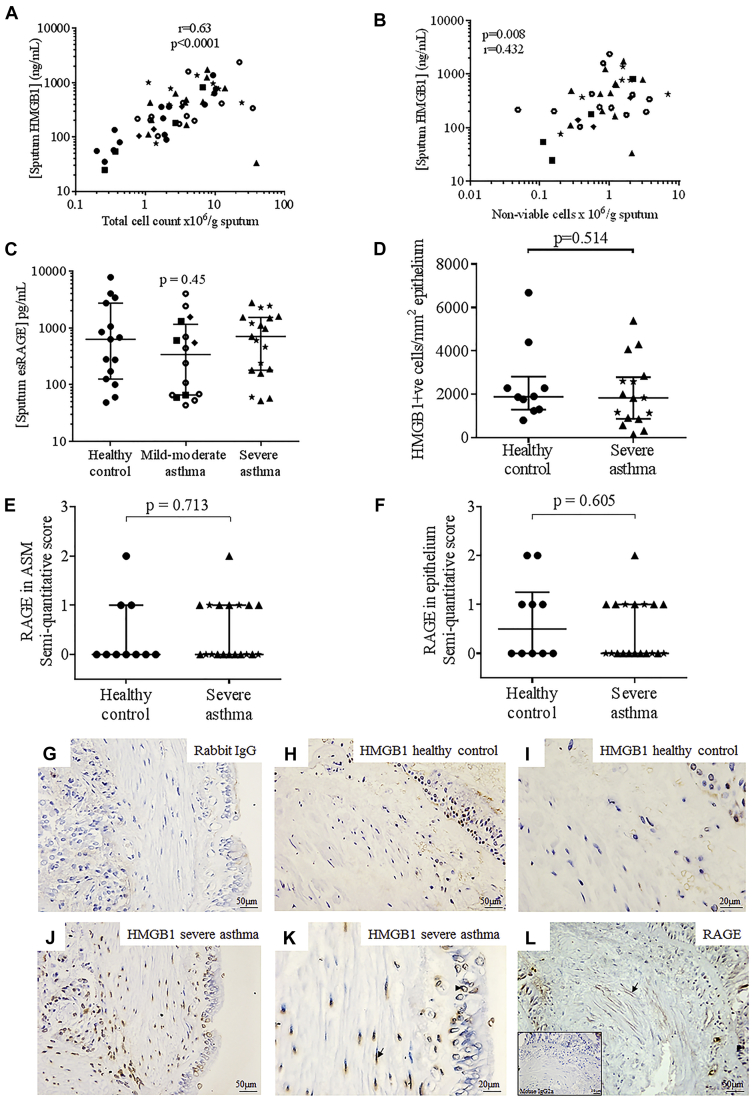
Fig E1.
Sputum HMGB1 correlated with sputum total cell count (A) and sputum nonviable cell count (B) in patients with asthma. C, Sputum esRAGE concentration in subjects with asthma and healthy controls. Horizontal bar represents geometric mean (95% CI). P value from Kruskall-Wallis test. Subject characteristics are presented in Table E2. D, The number of HMGB1+ cells/mm2 epithelium in bronchial biopsies. E and F, RAGE expression was assessed using a semi-quantitative scoring system: 0 = no positive staining; 1 = little positive staining; 2 = moderate positive staining; 3 = marked positive staining by a blinded observer in (Fig E1, E) ASM and (Fig E1, F) epithelium in bronchial biopsies. G-L, HMGB1/RAGE staining in bronchial tissue: G, Isotype control (rabbit immunoglobulin fraction, ×200 magnification), HMGB1 staining (brown) in a healthy control (H, ×200 magnification; I, ×400 magnification) and in a subject with severe asthma (J, ×200 magnification; K, ×400 magnification); positive staining was observed in the smooth muscle (arrow) and the epithelium (arrow head). L, RAGE staining in a tissue section from a patient with severe asthma showing RAGE expression in smooth muscle (arrow) and epithelium (arrowhead) at ×200 magnification. Inset: mouse IgG2a isotype control (×200 magnification). Subject characteristics are presented in Table E3. Symbol key: ● = healthy control; ■ = GINA 1; ◆ = GINA 2;  = GINA 3; ▲ = GINA 4; ★ = GINA 5. esRAGE, Endogenous secretory RAGE.
= GINA 3; ▲ = GINA 4; ★ = GINA 5. esRAGE, Endogenous secretory RAGE.