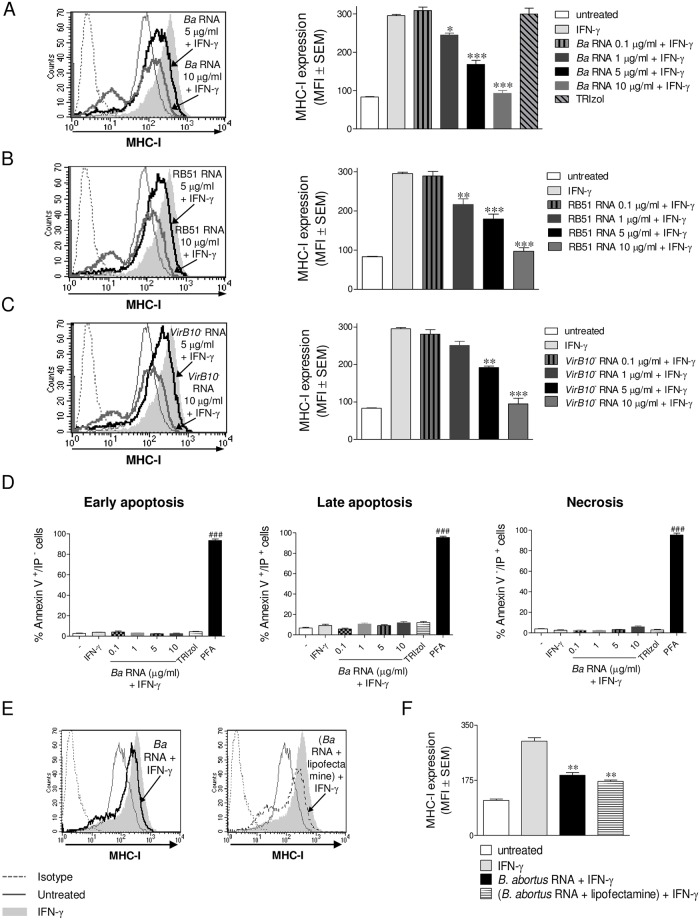
Fig 3. B. abortus RNA inhibits MHC-I expression and this does not involve loss of cell viability.
(A) THP-1 cells were treated with different doses of B. abortus WT RNA in the presence of IFN-γ for 48 h. THP-1 cells treated with TRIzol extracted products in the absence of bacteria were used as a control. (B and C) THP-1 cells were treated with different doses of RB51 (B) and virB10- (C) RNAs in the presence of IFN-γ for 48 h. MHC-I expression was assessed by flow cytometry. (D) THP-1 cells treated with different doses of B. abortus WT RNA in the presence of IFN-γ for 48 h were stained with Annexin V-FITC and Propidium Iodide (PI) and then analyzed for early Apoptosis (Annexin V+/PI-), late apoptosis (Annexin V+/PI+) and necrosis (Annexin V-/PI+). Cells treated with Paraformaldehyde (PFA) were used as a positive control. (E and F) THP-1 cells were transfected with B. abortus WT RNA with lipofectamine or treated with B. abortus WT RNA in the presence of IFN-γ for 48 h. MHC-I was assessed by flow cytometry. Bars represent the arithmetic means ± SEM of five experiments. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 vs. IFN-γ-treated. ###P<0.001 vs. untreated.