FIGURE 18.
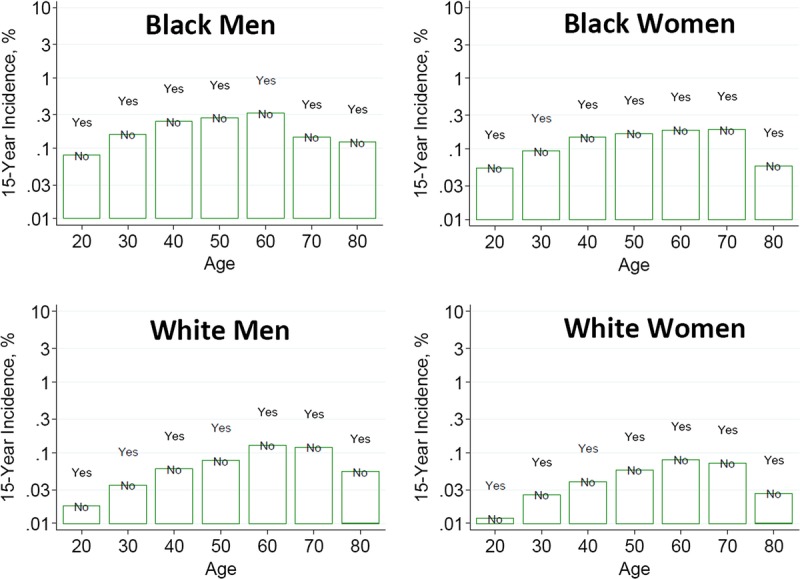
Estimated 15-year incidence (%) of ESKD in the United States according to non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus status and demographic profile from the CKD-PC. *The base-case scenario is defined as: age-specific eGFR (114, 106, 98, 90, 82, 74, and 66 mL/min per 1.73 m2 for ages 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 years, respectively), SBP 120 mm Hg, urine ACR 4 mg/g [0.4 mg/mmol], BMI 26 kg/m2, and no diabetes mellitus or antihypertensive medication use. These were selected as being representative of recent US living kidney donors where, with the exception of eGFR, there was little variation in health characteristics by age. ACR, albumin-to-creatinine ratio; BMI, body mass index; CKD-PC, Chronic Kidney Disease-Prognosis Consortium, eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESKD, end-stage kidney disease; SBP, systolic blood pressure. Reprinted from Grams ME, Sang Y, Levey AS, et al. Kidney-failure risk projection for the living kidney-donor candidate. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:411-421.7
