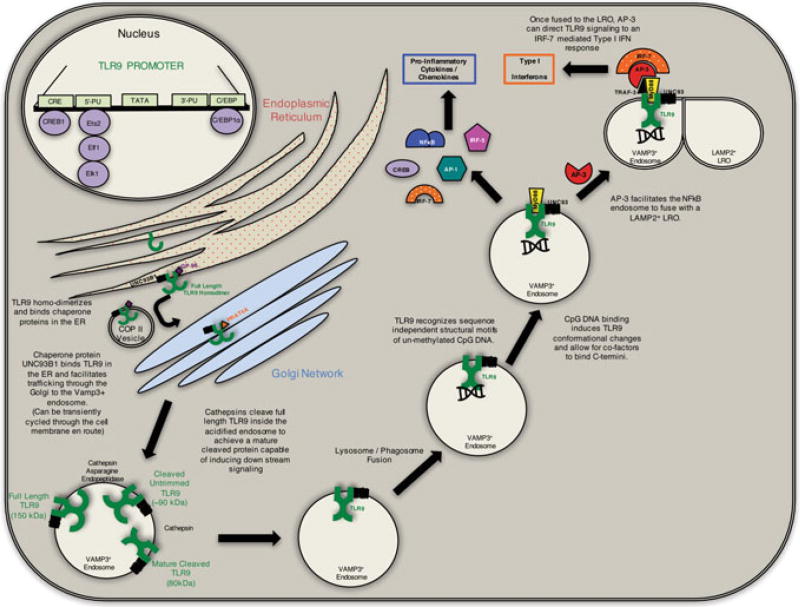
Fig. 1.
TLR9 regulation and signaling: TLR9 expression is regulated by cis and trans elements including the CRE site, 5′-PU box, 3′-PU box, and a C/EBP site. These sites bind the transcription factors CREB1, Ets2, Elf1, Elk1, and C/EBP1α. Full-length TLR9 (FL-TLR9) is then synthesized in the ER as a homodimer with the aid of chaperone proteins UNC93B1 and GP96. The full-length homodimer is then shuttled to the Golgi via a COPII vesicle where it binds the chaperone protein PRAT4a to facilitate trafficking. The fully synthesized FL-TLR9 is then incorporated into a VAMP3+ endosome where cathepsin and asparagine endopeptidases cleave the receptor to form the mature, cleaved form. This mature form of TLR9 is then free to induce downstream signaling cascades upon ligand binding. Cellular localization and interactions with adaptor proteins can further differentiate the type of signaling response upon binding its cognate ligand