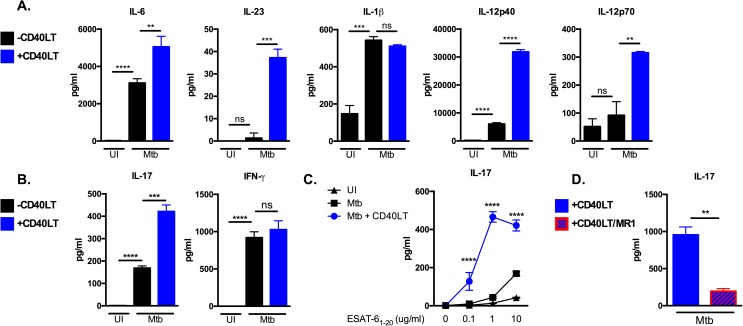
Fig 3. Engaging CD40 on DCs enhances antigen-specific IL-17 responses.
(A) B6 DCs were left uninfected or infected with Mtb in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml multimeric CD40LT reagent (CD40LT) for 24 hours. Cell-free supernatants were collected after 24 hours and the indicated innate cytokines were measured by ELISA. (B) DCs from (A) were pulsed with ESAT-61−20 at 10 μg/ml in the presence or absence of CD40LT and co-cultured with ESAT-6 TCR-Tg T cells for 72 hours. Supernatants were assayed for IL-17 and IFN-γ by ELISA. (C) B6 DCs were pulsed with increasing concentrations of ESAT-61−20 peptide (0, 0.1, 1.0 and 10 μg/ml) either left uninfected (UI) or infected with Mtb in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml CD40LT for 24 hours followed by co-culture with purified ESAT-6 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells for 72 hours. Supernatants were assayed for IL-17 by ELISA. (D) B6 DCs were pulsed with ESAT-61−20 peptide at 10 μg/ml and infected with Mtb in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml CD40LT for 24 hours. Co-culture with ESAT-6 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells was done in the presence or absence of 20 μg/ml anti-CD40L blocking antibody (clone MR1). Cell-free supernatants were collected after 72 hours and IL-17 levels determined by ELISA. Data are representative of 3–4 independent experiments. Values are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using a 2-tailed unpaired T-test. ** p<0.005, *** p<0.0005, **** p<0.0001, ns = not significant.