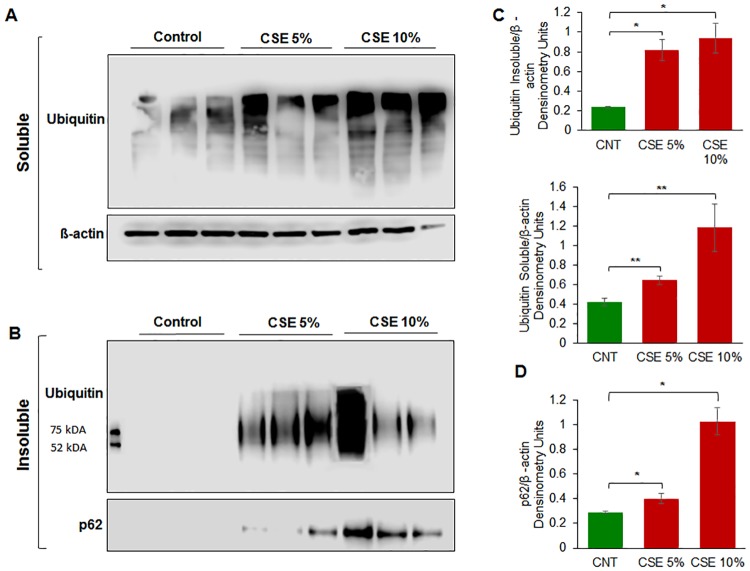
Fig 1.
A) ARPE-19 cells were treated with the indicated doses of CSE for 12 hours. CSE was observed to increase the amount of ubiquitinated-proteins in the soluble fraction as the dose of CSE increases, indicating that CSE increases protein synthesis. B) In the insoluble fraction, we see an increase in insoluble ubiquitinated-proteins. The data suggests that CSE results in an accumulation of ubiquitinated-proteins in aggresome bodies. We also observe increase in accumulation of p62 with increasing doses of CSE, indicating that CSE induces autophagy impairment. C) Densitometry analysis shows a statistically significant (p < 0.05) increase in ubiquitinated-proteins. The insoluble fraction shows a statistically significant (p < 0.01) increase in ubiquitinated proteins, suggesting that CSE results in aggresome formation. D) Densitometry analysis of p62 shows a statistically significant increase (p < 0.01) with higher CSE doses, indicating CSE induced autophagy impairment. From the data presented as above, we can conclude that CSE induces protein misfolding, ubiquitination, and aggregation resulting in aggresome formation. Data is presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05. ** p < 0.01 with n = 3 samples per group.