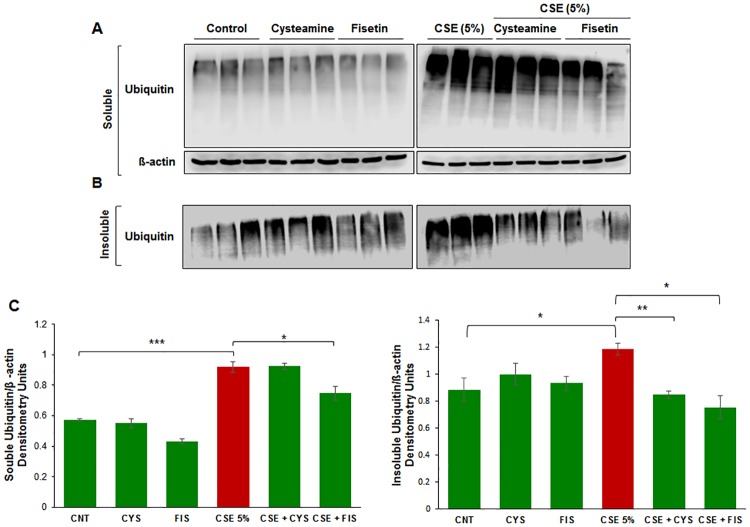
Fig 2.
A) ARPE-19 cells were treated with the indicated dose of CSE for 14 hours. Total protein extracts were isolated and separated into soluble and insoluble fractions, which were then immunoblotted for ubiquitin. In the soluble fraction, we observed an increased accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins with CSE treatment in comparison to control. B) We observe an increase in insoluble ubiquitinated proteins when ARPE-19 cells were treated with CSE in comparison to control cells. When ARPE-19 cells are treated with cysteamine (250 μM) or fisetin (40 μM), we observed a decrease in insoluble ubiquitinated proteins. C) Densitometry analysis shows a statistically significant (p value < 0.001) increase in soluble ubiquitinated proteins with CSE treatment, and a significant decrease (p < 0.05) with only cysteamine treatment. Densitometry analysis of the insoluble fraction shows a statistically significant (p < 0.05) increase in insoluble ubiquitinated proteins with CSE treatment, and a statistically significant decrease in insoluble ubiquitinated proteins with either cysteamine (250 μM, p <0.01) or fisetin (40 μM, p < 0.05). From the data presented, we can conclude that cysteamine or fisetin treatment can ameliorate CSE induced insoluble ubiquitinated-protein accumulation in ARPE-19 cells. Data is presented as ± SEM. * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01 *** p < 0.001 with n = 3 samples per group.