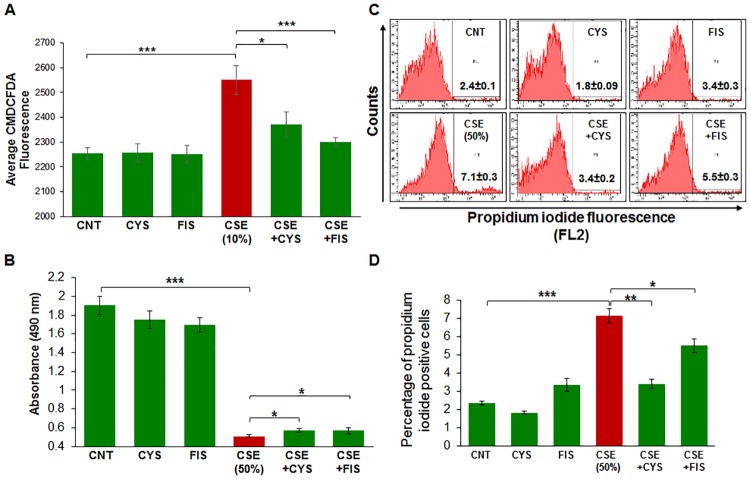
Fig 6.
A) ROS production was assessed in ARPE-19 cells that were exposed to room-air or CSE (10%) and/or treated with cysteamine (250 μM) or fisetin (40 μM). CSE significantly induced ROS production and treatment with cysteamine (250 μM, p < 0.05) or fisetin (40 μM, p < 0.001) significantly reduced the production of ROS. The cell viability of ARPE-19 cells was assessed by MTS-based proliferation assay (B) or propidium iodide exclusion assay (C, D). Treatment of ARPE-19 cells with CSE (50%) resulted in significantly diminished cell viability (p < 0.001), while cysteamine (250 μM) and fisetin (40 μM) treatment resulted in significant rescue in cell viability and ameliorated the deleterious effects of CSE (p < 0.05). Data is presented as ± SEM. * p < 0.05 *** p < 0.001 with n = 8 samples per experimental group.