Figure 1.
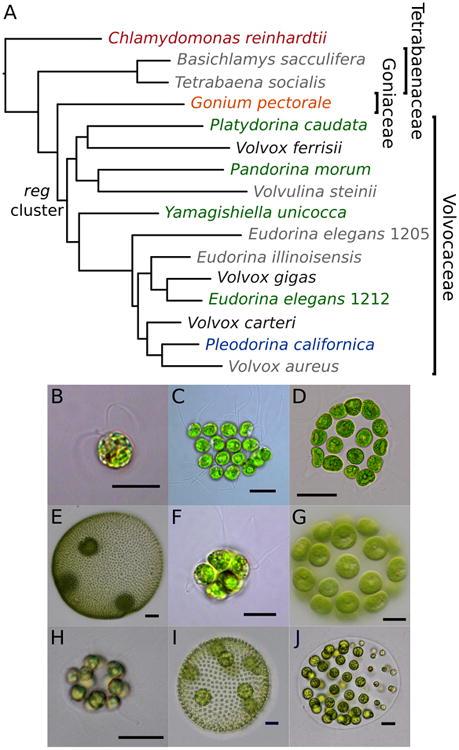
Species phylogeny and micrographs of exemplar species of volvocine algae. A. Bayesian species tree, consistent with previously published species trees. Color of species without (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, red; Gonium pectorale, orange) and with the reg cluster (undifferentiated Pandorina morum, Platydorina caudata, Yamagishiella unicocca, Eudorina elegans UTEX 1212, green; soma differentiated Pleodorina californica, blue) correspond to other figures, Volvox (germ and soma differentiated) species for which the reg cluster has been previously sequenced are shown in black species in grey are not included in this analysis. Note that numbers following E. elegans species refer to UTEX strain numbers. Inferred origin of the reg cluster is denoted. See Figure 5 for maximum likelihood and Bayesian support values. B. C. reinhardtii (scale bar, 10 μm); C. G. pectorale (10 μm); D. Pla. caudata (25μm); E. V. ferrisii (50 μm); F. Pan. morum (10 μm); G. Y. unicocca (20 μm); H. E. elegans UTEX 1212 (10 μm); I. V. carteri f. nagariensis (50 μm); J. Ple. californica (25 μm).
