Figure 6.
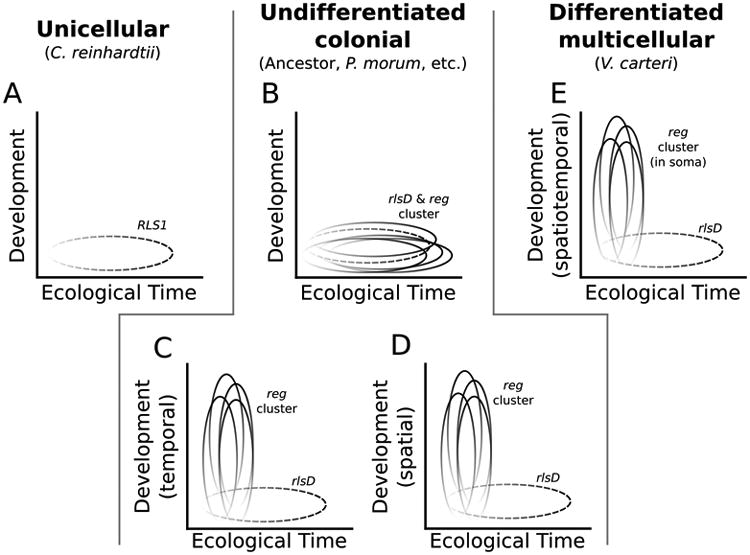
Conceptual schematic of hypothesized VARL gene expression patterns in unicellular, undifferentiated, and differentiated species. A. Temporal expression of RLS1 (dashed) in C. reinhardtii in response to environmental change. B. The reg cluster (shown as four genes, though some species have five reg cluster genes) maintains expression in response to environmental change following its origin from the duplication of rlsD (dashed). C. The reg cluster is developmentally co-opted to control cell division throughout the life cycle. D. The reg cluster is developmentally co-opted to control the AP axis. Panels B, C, and D are not mutually exclusive as different hypotheses may apply to different undifferentiated species and a single hypothesis may not uniformly apply to all genes within the reg cluster of a given species. E. The reg cluster is co-opted to regulate somatic differentiation in V. carteri. For all panels, darker shading represents higher gene expression.
