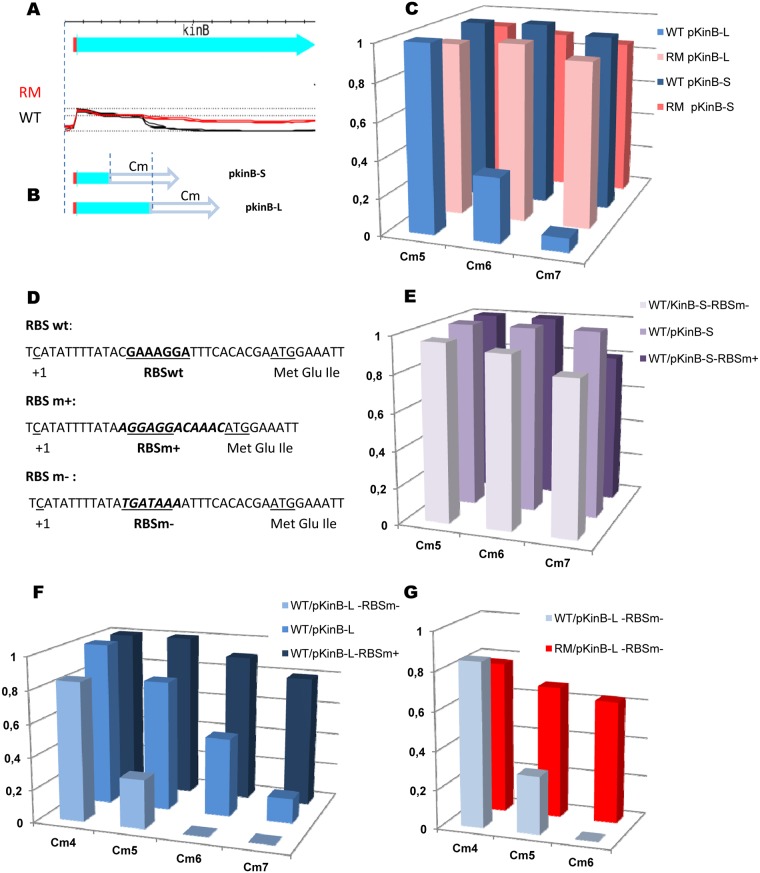
Fig 8. B. subtilis kinB gene contains intragenic Rho-dependent terminator.
(A and B) Schema of the experimental design used for analysis of the kinB putative Rho-dependent terminator. (A) Cartoon of the kinB expression unit and the expression profiles of kinB in the WT (black) and RM (red) cells [17]. (B) Transcription initiation region (small red rectangle) and the 5’-terminal parts of kinB gene were cloned at the plasmid pGKV210 [116] upstream the promoter-less chloramphenicol-resistance gene (open arrow). The cloned fragments are delineated by the dotted lines. (C) Rho activity determines cellular resistance to chloramephenicol. B. subtilis BSB1 WT and RM cells containing pKinB-Short (pKinB-S) and pKinB-Long (pKinB-L) plasmids were grown to OD 0.5 and platted in sequential dilutions at the LB-plates containing or not chloramphenicol (Cm) at the indicated concentrations (μg/ml). Cm-resistant cells were scored after 24 hours of incubation at 37°C and compared to total number of viable cells. The bars represent average values from three independent experiments totally including twelve biological replicas for each strain. (D-G) Initiation rate of kinB translation negatively affects efficiency of Rho-dependent intragenic termination of kinB transcription. (D) Nucleotide sequence of the translation initiation regions (TIR) carrying native (RBSwt; [112]) and the modified strong (RBSm+) or weak (RBSm-) ribosome binding sites. The RBS sequences are bolded and underlined. The whole modifications of TIR sequences are bolded and in italics. The kinB transcriptional start (+1) and ATG codon are underlined. (E, F) B. subtilis BSB1 WT cells carrying pKinB-S or pKinB-L plasmids with different kinB RBS (RBSwt, RBSm+ and RBSm-) were analyzed for Cm-resistance as described in (C). (E) Modifications of kinB RBS have no effect on Cm-resistance when plasmids do not contain transcription terminator within kinB (pKinB-S). (F) In the presence of kinB transcription terminator, the level of Cm-resistance depends on the strength of kinB RBS (pKinB-L). (G) The pKinB-L-RBSm- plasmid with a weak RBS determines high level of Cm-resistance after Rho inactivation in RM cells. Each experiment depicted in (E-G) included three biological replicas of each strain and was repeated at least three times. The data for WT cells with pKinB-S and pKinB-L plasmids presented in (E) and (F) are independent from (C).