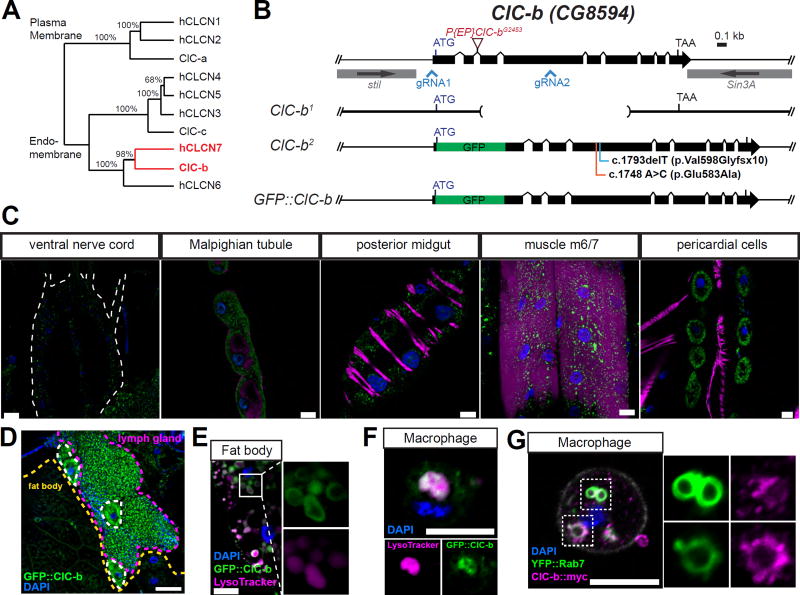
Figure 1. Ubiquitous expression of ClC-b and its localization to endolysosomes in macrophages.
(A) Phylogeny of human and Drosophila chloride transporters proteins. Numbers shown are bootstrap test values (%). ClC-a, -b, and -c are annotated Drosophila chloride channel family subunits according to Flybase (http://flybase.org). Highlighted in red are the genes of interest of the current study. (B) The ClC-b genomic locus and alleles used in the study. (C) GFP::ClC-b expression in larval tissues. Larval tissues were fixed and stained with anti-GFP (green), phalloidin for actin (magenta), and DAPI for nuclear DNA (blue). Scale bars represent 20 µm. (D) GFP::ClC-b expression in larval lymph glands and fat bodies. GFP single was not amplified by using primary or secondary antibodies. Scale bar represents 50 µm. (E and F) LysoTracker staining in fat body (E) and macrophages (F) isolated from GFP::ClC-b larvae. Scale bars represent 10 µm. (G) Macrophages isolated from larvae expressing ClC-b::myc and YFP::Rab7 with Cg-GAL4 driver. Scale bar represents 10 µm.