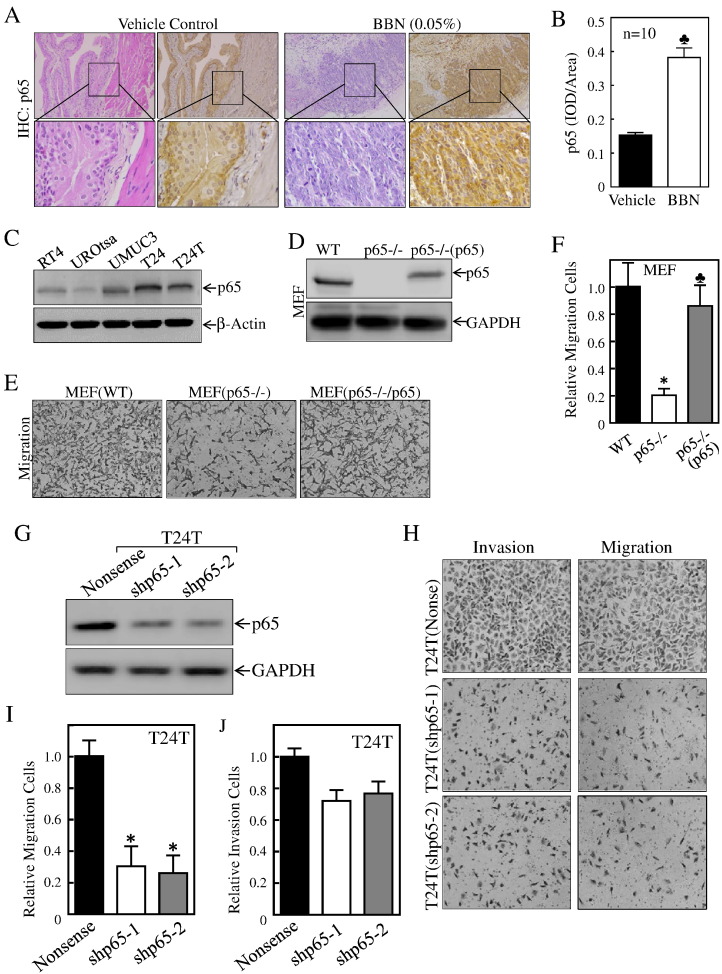
Figure 1.
p65 was overexpressed in BBN-induced high invasive mouse BCs and human BC cell lines and promoted BC cell migration.
(A) HE staining and IHC staining were performed to evaluate morphology and p65 expression in BBN-induced mouse invasive BCs; the IHC images were captured using the AxioVision Rel.4.6 computerized image system as described in “Materials and Methods”. (B) The p65 protein expression levels were analyzed by calculating the integrated IOD/area using Image-Pro Plus version 6.0. The Student's t test was utilized to determine the P value; and the symbol (♣) indicates a significant increase from vehicle-treated mice (*P < .05) (n = 10). (C & D) Whole cell extracts from the indicated cells were subjected to Western blot for determination of p65 protein expression. (E & F) The migration abilities of MEF(WT), MEF(p65−/−), and MEF[p65−/−(p65)] were determined by using BD BioCoat Matrigel Migration Chamber without the Matrigel. The bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Student's t test was utilized to determine the P value. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant decrease as compared with MEF(WT) cells (*P < .05), and the symbol (♣) indicates a significant increase as compared with MEF(p65−/−) cells (♣P < .05). (G) p65 knockdown constructs were stably transfected into T24T cells. The knockdown efficiency of p65 protein was assessed by Western blotting. (H-J) The migration and invasion abilities of T24T(shp65) transfectants were evaluated in comparison to their scramble vector transfectant T24T(nonsense). (I) The bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Student's t test was utilized to determine the P value; the asterisk (*) indicates a significant decrease in comparison to scramble vector transfectants (*P < .05). (J) The invasion rate was normalized with the insert control according to the manufacturer's instruction. The bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Student's t test was utilized to determine the P value, P > .05.