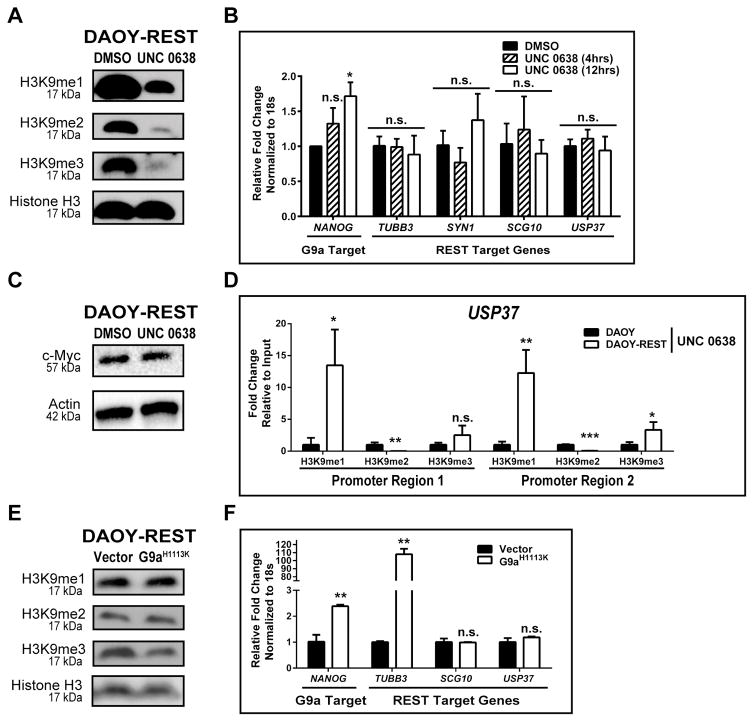
Figure 5. REST elevation counters de-repression of target genes by G9a inhibition.
A. DAOY-REST cell extracts were subjected to Western blot analyses to measure levels of histone H3K9-me1, -me2, and -me3 following exposure to 1.1 μM UNC 0638 (or DMSO) for 12 hrs. Total histone H3 served as the loading control. B. Changes in the expression of G9a and REST-target genes in DAOY-REST cells treated with 1.1 μM UNC 0638 was shown by Q-RT-PCR. C. Western blotting analysis was performed to measure the levels of the GLP target protein c-Myc following treatment of DAOY and DAOY-REST cells with a 48hrs-IC50 dose of UNC 0638 (1.1 μM) for DAOY cells. β-actin was used as a loading control. D. ChIP assays were performed to demonstrate residual histone H3K9-me1, -me2, and -me3 within USP37 promoter regions-1 and -2 in DAOY-REST cells relative to DAOY cells following drug treatment. Data shown as fold change relative to input. E. Western blotting was performed to assess global changes in G9a-dependent histone H3K9-me1, -me2, and -me3 in DAOY-REST cells transduced with G9aH1113K or vector (control). Histone H3 was used as loading control. F. Q-RT-PCR to assess expression of known G9a and REST-target genes in DAOY-REST cells ectopically expressing mutant G9aH1113K. (*=p<0.05, **=p<0.01, ***=p<0.001, and n.s. = not significant).