Fig. 2. Schematic depiction of allosteric modulation of a GPCR.
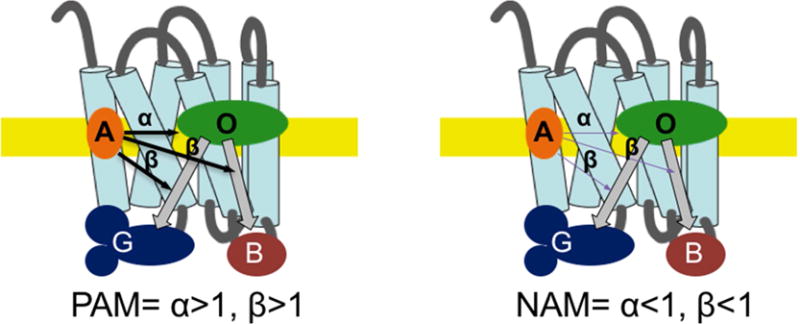
Classically, an orthosteric agonist (O) binds to the GPCR and facilitates signaling through several G protein (only one shown for clarity) and non-G protein pathways (G and B, respectively). The relative strength of signaling often varies among signaling pathways (functional selectivity).An allosteric modulator (A) will bind to the receptor at a site independent from the orthosteric site. The allosteric modulator may positively (PAM) or negatively (NAM) influence orthosteric ligand binding (α) and/or signaling pathways (β), as depicted by thick and thin arrows and discussed in the text.
