Figure 1.
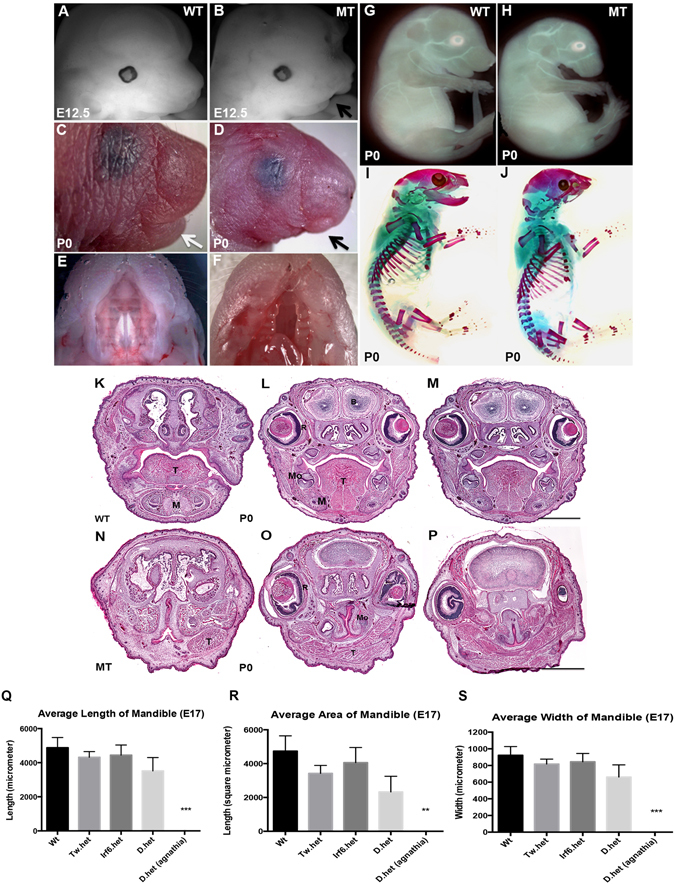
Craniofacial abnormalities in Irf6 and Twist1 double heterozygotes murine animals and morphometric measurements of embryonic mandible. Compared to wild type murine embryo (A), littermate mutant embryo of double het (B) has a short mandibular prominence start at E12.5. At P0, mutant pup has lower jaw abnormalities (C versus D), and complete cleft of the secondary palate (E versus F). Phase contrast images show mutant embryo with absent lower jaw and low-set ear (H) but grossly normal body (G versus H). Skeletal preparations show that the mutant pup is missing a mandible and has abnormalities in inner ear bones (I versus J). Hematoxylin and eosin staining of coronal sections of heads from wild type (K–M) and double heterozygous affected murine pups (N–P), from anterior (K,N), middle (L,O) to posterior (M,P). Relative to wild type littermate (WT), mutant (MT) has cleft palate, malformed tongue, detached retina and holoprosencephaly (O,P). Tongue (T), mandible (M), molar tooth germ (Mo), retina (R), brain (B). Scale bars = 1000 μm. Figures (Q,R and S) are average length, width and area of murine mandibles of different genotypes at E17.5. A total of 28 craniofacial skeletons of murine embryos were used to calculate the averages. The black bars represent standard error for each genotype. Average mandibular lengths of murine embryos of all different genotypes (Q). Average mandibular widths of murine embryos of all different genotypes (R). Average mandibular area of murine embryos of all different genotypes (Q). The average area of Irf6, Twist1 double hets vs. wild type is smaller relative to mean area of wild types, but the difference is not statistically significant using the multi-variants ANOVA test. Wild type (WT), Twist1 heterozygous (Tw.het), Irf6 heterozygous (Irf6.het) and double heterozygous (D.het).
