Figure 2.
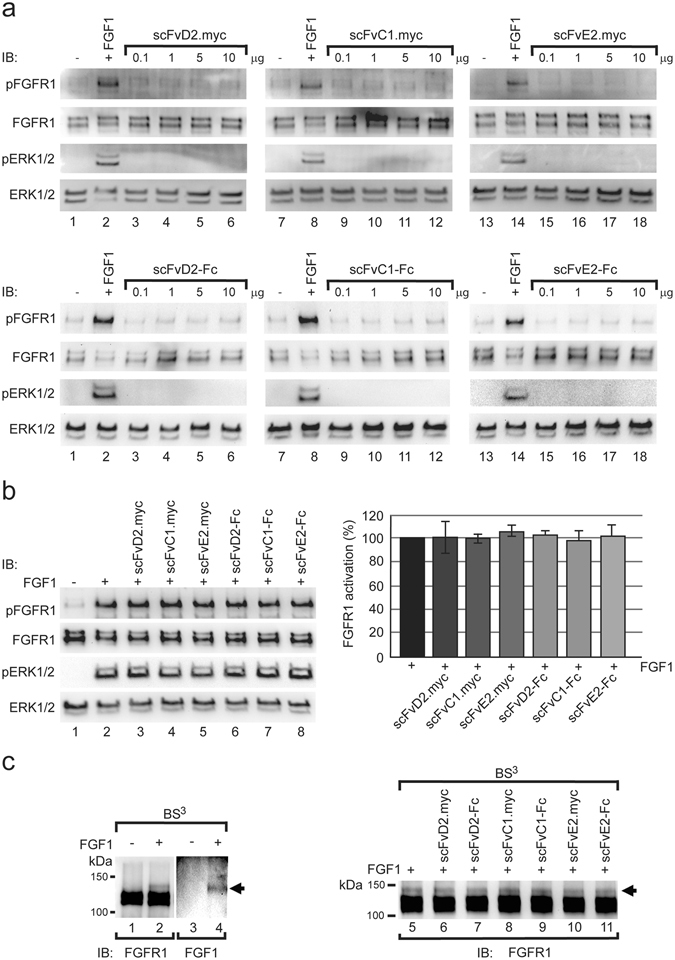
Antibody fragments do not disturb the FGFR1 function. (a) Serum starved NIH3T3 cells were stimulated with FGF1 and increasing doses of antibody fragments. The activation of FGFR1 was assessed by Western blotting using antibodies against phosphorylated FGFR1 (pFGFR1), phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2), total FGFR1 and total ERK1/2 (loading controls). (b) Antibodies in the scFv and scFv-Fc formats have no influence on the FGFR1 activation. Serum starved NIH3T3 cells were stimulated for 15 min with FGF1 alone or in the presence of 10x molar excess of antibody fragments. Cells were lysed and the level of phosphorylated FGFR1 and ERK1/2 (pFGFR1 and pERK1/2) and total level of ERK1/2 and FGFR1 (loading controls) was assessed using specific antibodies and quantified (n = 3, error bars represent SD). (c) FGF1-FGFR1 interaction monitored with chemical crosslinking. U2OSR1 cells were incubated with FGF1 and crosslinked with BS3. FGF1-FGFR1 crosslinking product was formed that was detected both with anti-FGFR1 and anti-FGF1 antibodies (left panel, arrow). The influence of antibody fragments on the FGF1-FGFR1 interaction was monitored with chemical crosslinking. U2OSR1 cells were incubated with FGF1 in the presence or absence of various antibodies and subjected to crosslinking with BS3. Formation of FGF1-FGFR1 complex was monitored by Western blotting using anti-FGFR1 antibodies. Cropped blots were displayed, full size blots are included in Supplementary Information.
