Figure 3.
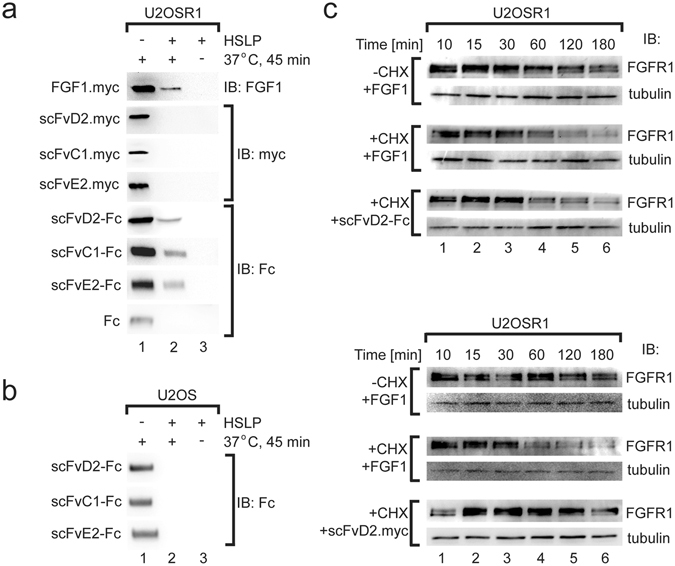
Bivalent scFv-Fc antibodies are internalized into cells in the FGFR1-dependent manner. (a) Antibodies in the bivalent scFv-Fc format are internalized into cells that overproduce FGFR1. Serum starved U2OSR1 cells, that overproduce FGFR1 were incubated with FGF1.myc, scFv.myc proteins or scFv-Fc antibody fragments to allow for formation of antibody-FGFR1 and FGF1.myc-FGFR1 complexes. Cells were then shifted for 45 min to 37 °C to initiate internalization. The internalization reaction was stopped by cooling down the cells on ice. The surface bound FGF1.myc or antibody fragments were removed by washing with low pH buffer containing high salt concentration (HSLP) and internalized FGF1.myc, scFv.myc and scFv-Fc proteins were recovered from cell lysates with anti-c-Myc (for FGF1.myc and scFv proteins) and Protein A Sepharose (for scFv-Fc proteins). Internalized proteins were detected by Western blotting using specific antibodies. (b) Internalization of scFv-Fc antibody fragments is strictly dependent on the level of FGFR1. Control U2OS cells that contain only very low level of FGFR1 were not able to internalize scFv-Fc proteins. (c) FGF1 and bivalent scFv-Fc antibody fragments stimulate FGFR1 degradation. Serum starved U2OSR1 cells were incubated with FGF1, scFvD2 or scFvD2-Fc in the presence or absence of cycloheximide (CHX). Cells were lysed and the level of FGFR1 was assessed by Western blotting. Tubulin was used as a loading control. Cropped blots were displayed, full size blots are included in Supplementary Information.
