Figure 6.
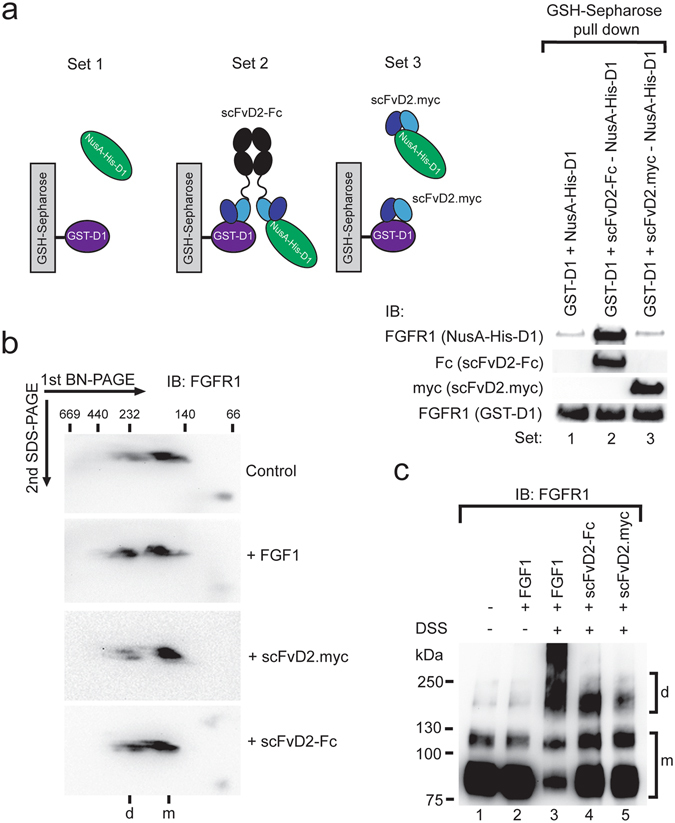
The bivalent scFvD2-Fc antibody fragment induce FGFR1 dimerization. (a) The bivalent scFvD2-Fc antibody can simultaneously bind two D1 domains of FGFR1. Purified his-tagged, NusA fusion of domain D1 of FGFR1 (NusA-His-D1) was incubated either alone or in the presence of the bivalent scFvD2-Fc or monovalent scFvD2.myc. Next, preformed antibody fragment-NusA-His-D1 complexes were incubated with purified GST fusion of D1 domain of FGFR1 (GST-D1). Proteins bound to the GST-D1 were analyzed by Western blotting using specific antibodies. The interaction of D1 domains with each other is strongly enhanced only in the presence of the bivalent scFvD2-Fc. (b) Oligomeric state of FGFR1 was studied with 2D BN/SDS PAGE. Serum starved NIH3T3 cells were treated with FGF1, scFvD2.myc or scFvD2-Fc. Membrane proteins were solubilized with digitonin and separated in the 1st native dimension using 4–13% BN-PAGE gels. Native gels were sliced and separated in the 2nd denaturing dimension using SDS-PAGE. Oligomeric state of FGFR1 was assessed by Western blotting using FGFR1-specific antibodies. (c) Chemical crosslinking reveals that the bivalent scFvD2-Fc antibody fragment can induce FGFR1 dimerization in cells. Serum starved NIH3T3 cells were incubated with FGF1, scFvD2.myc or scFvD2-Fc and crosslinked with DSS. Cells were lysed, FGFR1 was isolated by co-immunoprecipitation and oligomerization of FGFR1 was assessed by Western blotting using receptor-specific antibodies. Addition of FGF1 strongly induces FGFR1 dimerization. The bivalent scFvD2-Fc also induces FGFR1 dimerization, but to the lower extent than FGF1. In contrast the monovalent scFvD2.myc has no impact on the oligomeric state of FGFR1.
