Fig. 6.
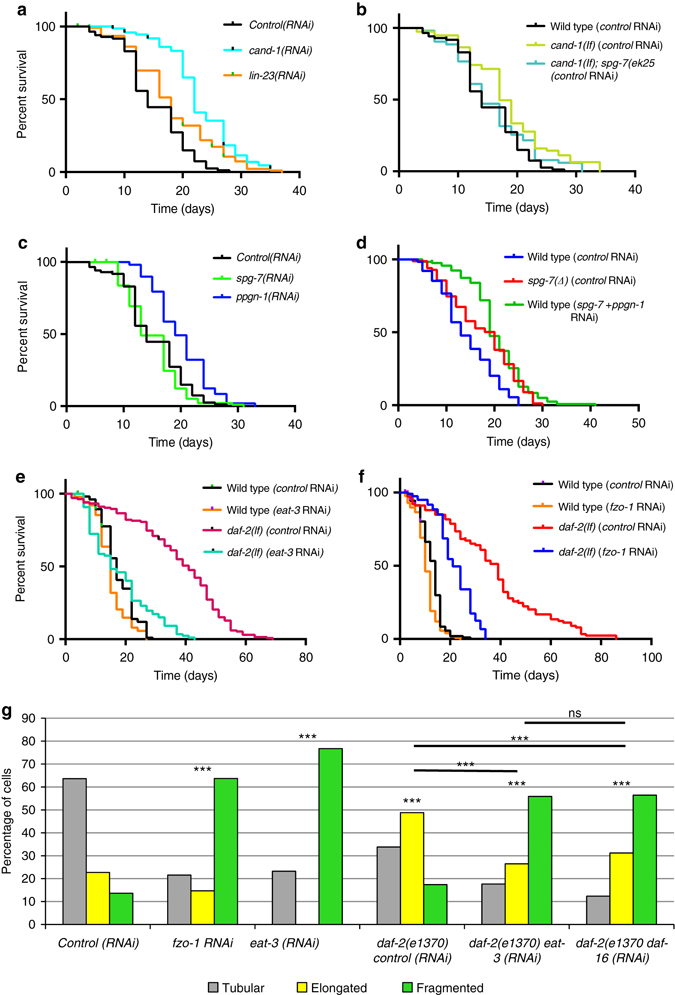
Increased mitochondrial elongation extends lifespans. a–e Survival curves for adults of the indicated RNAi treatments. The wild-type survival curves for a–c were analyzed at the same time and are shown in each panel for comparison. RNAi depletions of lin-23 a, cand-1 a, ppgn-1 c, and spg-7 + ppgn-1 d significantly increased mean lifespan. b cand-1 mutants and spg-7(tm2312) mutants d had increased the mean lifespan relative to wild type, while cand-1; spg-7(ek25) c animals had lifespan comparable to wild type. e, f eat-3 RNAi e and fzo-1 RNAi f depletions significantly decreased the mean lifespan of daf-2(e1370) mutants. All lifespan experiments were performed with four biological replicates. See Supplementary Table 2 for statistics. g The percentages of muscle cells with predominantly tubular, elongated, or fragmented mitochondria in adult hermaphrodites of the indicated genotypes/RNAi treatments visualized by mitochondria-targeted GFP expression in body-wall muscle cells. P values were determined by χ 2-test. Sample size (n) of muscle cells from left to right are: 278; 102; 179; 207; 136; 218. Mitochondrial morphology was scored blinded. The wild-type control from Fig. 1c was analyzed at the same time and is shown here for comparison. Asterisks above bars denote P value comparisons to wild type/control; asterisks above lines denote comparisons under the lines: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns = not significant
