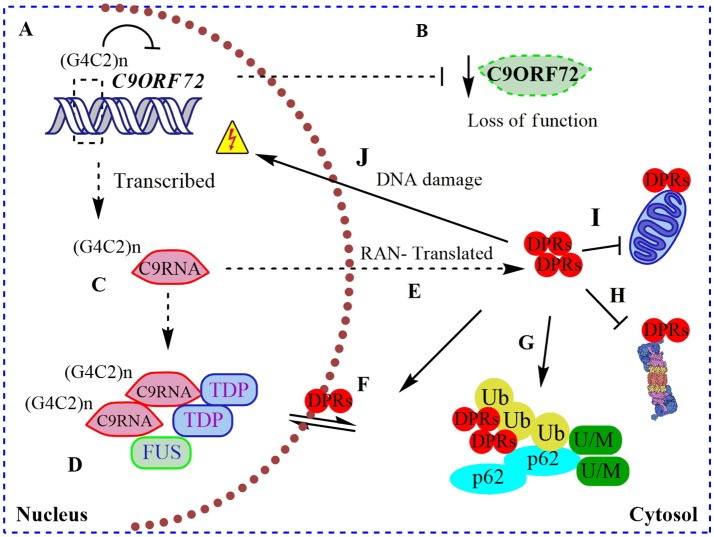
Figure 1.
Pathogenic roles of C9ORF72 in ALS and FTD. (A) Pathogenic GGGGCC repeat extensions [in the figure showed as (G4C2)n] can inhibit the transcription of endogenous C9ORF72, resulting in (B) diminished levels of C9ORF72 protein (loss of function); (C) (G4C2)n C9ORF72 can be both aberrantly sense and antisense transcribed to (G4C2)n C9RNA; (D) RNA foci containing these (G4C2)n C9RNA are found in the nucleus of C9ALS/FTD patients, sequestering RNA-binding proteins, such as TDP-43, and FUS, increasing the RNA processing dysfunction in ALS (gain of a RNA toxic function). (E) Also, (G4C2)n C9RNA are Repeat Associated Non-ATG (RAN) translated in toxic dipeptide repeat proteins (DPRs), contributing to the gain of a protein toxic function through (F) disruption of nuclear/cytosol transport by DRPs binding nuclear pore proteins; (G) DRPs are present in cytosolic protein inclusions in affected neurons, together with SQSTM1/p62, poly-ubiquitined proteins (Ub) and unfolded/misfolded (U/M) proteins; (H) bind to and inhibit the proteasome; (I) bind to and contributes to mitochondria dysfunction; and (J) cause DNA damage.