Figure 7.
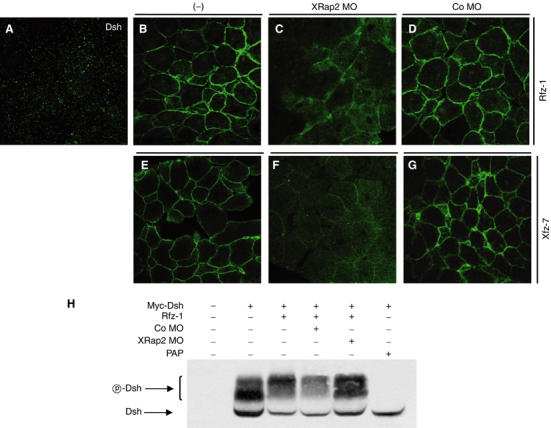
XRap2 is required for the translocation and phosphorylation of Dsh induced by frizzled signaling. (A) Ectopic GFP-Dsh is distributed in a punctate fashion in animal cap cells. XRap2 MO inhibits the relocalization of GFP-Dsh to the plasma membrane caused by rat Fz-1 (B, C) or Xenopus Fz-7 (E, F). Co MO has no effect on Dsh localization (D, G). (−), control without MO injection. (H) XRap2 depletion inhibits the phosphorylation of Dsh by Rfz-1 signaling. For phosphatase treatment, the immunoprecipitate from early gastrulae injected with myc-Dsh was incubated with potato acid phosphatase (PAP). (A–H) Four-cell stage embryos were injected into the animal pole region with RNAs, MO or a combination as indicated. Animal caps were cut from late blastulae and immediately fixed or subjected to Western blot. The subcellular localization of GFP-Dsh was analyzed by confocal microscopy. The amount of injected reagents is as follows: GFP-Dsh, 500 pg; rat Fz-1, 500 pg; Xenopus Fz-7, 500 pg; Myc-Dsh, 2 ng; XRap2 MO, 40 ng; Co MO, 40 ng.
