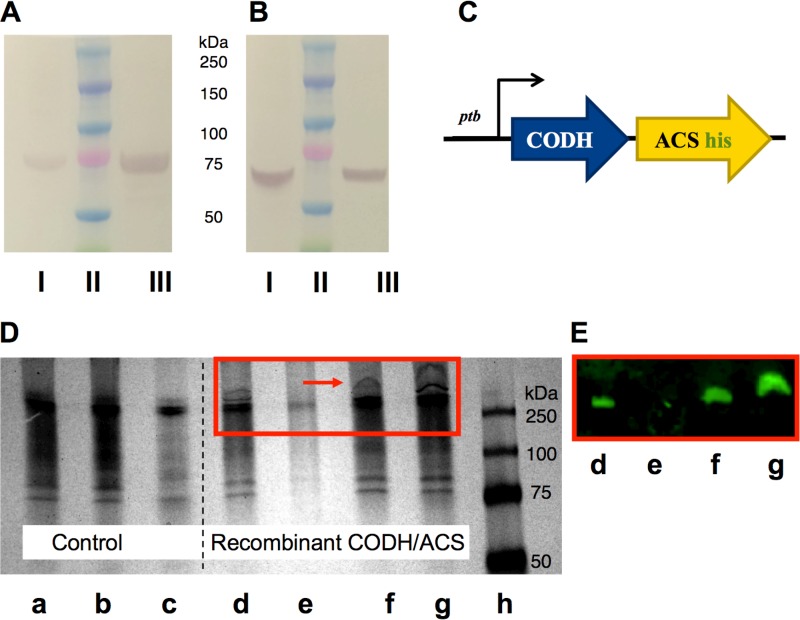
FIG 1.
Protein expression analysis of the heterologously expressed CODH/ACS enzyme complex in C. acetobutylicum using His tag purification, SDS-PAGE, and native PAGE. (A and B) Cell lysates were purified on a Ni-NTA column under native conditions. The purified fraction was loaded onto an SDS-PAGE gel and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. Two blots were probed against the ACS subunit (∼77.5 kDa) (A) or against the CODH subunit (∼67.6 kDa) (B) using polyclonal antibodies. I, whole-cell lysates from C. carboxidivorans (positive control); II, protein ladder; III, His tag-purified CODH/ACS protein from C. acetobutylicum under native conditions. (C) Schematic representation of the CODH/ACS expression cassette. Both subunits are under the control of the Pptb promoter, and the ACS subunit contains a His tag prior to the stop codon. (D) Native PAGE gel of wild-type (WT) C. acetobutylicum (control) and C. acetobutylicum expressing CODH/ACS. a, whole-cell extract control; b, insoluble cell extract fraction of control; c, soluble cell extract fraction of control; d, whole-cell extract of strain expressing CODH/ACS; e, insoluble cell extract fraction of strain expressing CODH/ACS; f and g, soluble cell extract fraction of strain expressing CODH/ACS (early and late stage of growth, respectively); h, protein ladder. (E) Western blot of native gel shown in panel D (d to g), whereby the blot was probed with anti-6× His tag and Alexa Fluor 647 antibodies to show that the high-molecular-weight band seen on native PAGE gel is that of the CODH/ACS tetrameric complex.