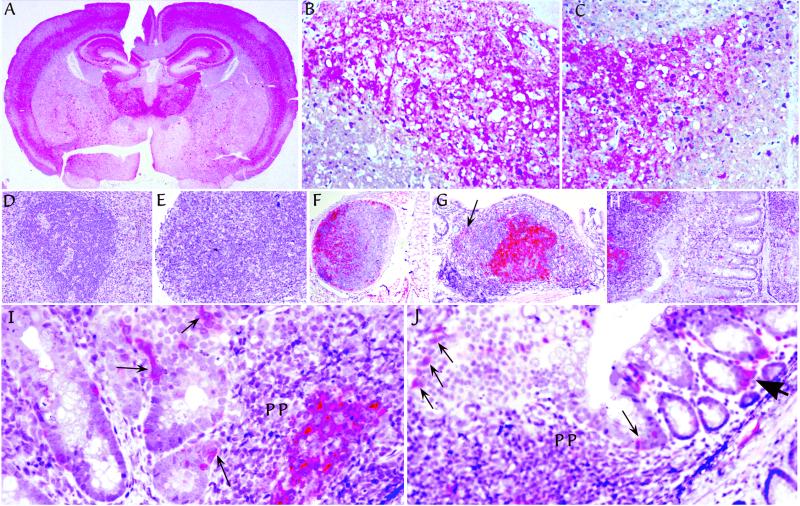
Figure 3.
Pathologic PrP (red) in tissues from representative Tg mice after i.p. infection. (A) Typical distribution after FU-CJD infection of mice. This example is from a mIg Tg mouse killed at 223 days. Comparable pathology was found in intracerebral infections with no abnormal PrP found in age-matched uninoculated controls (ref. 24 and data not shown). Higher-power examinations of comparable hippocampal regions, from a mIg Tg mouse at 236 days (B), and a JhD mouse at 212 days (C), show spongiform change with fine and coarse deposits of pathologic PrP. Typical spleen (D) and mesenteric lymph node (E) in a JhD B cell deficient mouse at 212 days show lymphoid disorganization and absence of FDCs by PrP staining. Normal FDCs were also not detectable by S-100 protein staining in JhD mice (data not shown). In contrast, FDCs have abundant pathologic PrP in lymph nodes of (m+s)Ig Tg mice, including a distant lymph node in lung at 199 days (F), and in a Peyer's patch of the ileum at 177 days (G). Arrow in G points to one of many PrP-positive small cells dispersed outside the germinal center with a dendritic-to-macrophage morphology. Pathologic PrP was equally abundant on FDCs of mIg Tg mice without secreted Ig, as shown at 223 days in Peyer's patch at the left in H. mIg Tg mice (but not JhD or uninfected mice), also showed PrP-positive cells in epithelium in the region of Peyer's patches as in I (arrows). Some of these interspersed cells are consistent with M cells. Similar M cells are seen in a row just above lymphoid cells of a Peyer's patch at low-power (thin arrows in J). J also shows labeled single cells with a dendritic morphology in the lamina propria adjacent to glands at the lumen, as well as clusters of dendritic cells (large arrowhead).