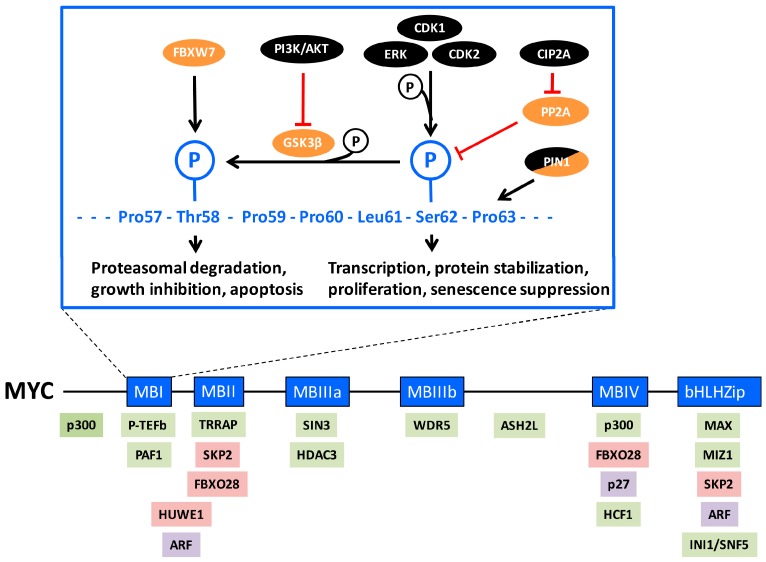
Figure 1.
MYC structure and interaction partners. Lower part: The structure of MYC with evolutionary conserved regions of MYC, including the MYC boxes (MB) 1–4 and basic region/helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper (bHLHZip) domain, are depicted as blue boxes. Proteins of interest for this review interacting with respective regions, including regulators of transcription/chromatin, components of E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes and proteins with other functions described in the text are indicated in light green, pink or violet, respectively. Upper part: Enlargement of MB1. Proteins involved in regulation of the phosphorylation status of threonine-58 (Thr-58) and serine-62 (Ser-62), and the biological output of these phosphorylations are indicated. Ser-62, which plays a role in regulating protein stability, transcription, proliferation and oncogenesis, is phosphorylated by indicated kinases. This phosphorylation facilitates glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β)-mediated phosphorylation of Thr-58, which is a signal for F-box protein FBX7-mediated proteasomal degradation linked to growth suppression and apoptosis. The activity of GSK3β is blocked by phosphorylation via the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway. The phosphorylation status of Ser-62 is also regulated by the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) with assistance from the PIN1 prolyl isomerase acting on proline-53 (Pro-53). PP2A can be blocked by endogenous inhibitory proteins such as cancerous inhibitor of PP2A (CIP2A). Proteins, depicted in black, represent factors with growth-promoting/oncogenic function, while those in orange represent growth/tumor-suppressive function in this context. PIN1, which plays a dual function, is depicted partly in black and partly orange. See the text for further explanation.