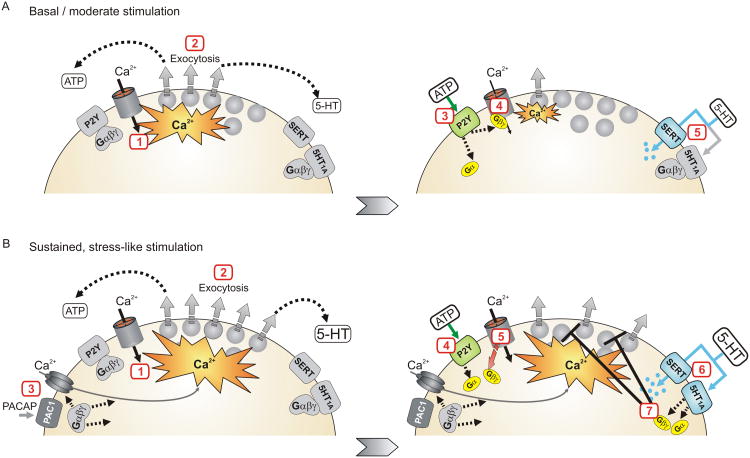
Figure 3. Proposed model in which serotonergic inhibition is fine-tuned to control stress-evoked catecholamine secretion.
A) During periods of basal or brief stimulation purinergic (and other) receptors that inhibit voltage-gated Ca2+channels mediate autocrine regulation of exocytosis. Left panel: 1) Acetylcholine released from the splanchnic nerve depolarizes chromaffin cells opening voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. 2) The Ca2+ entry triggers exocytosis of catecholamines and other transmitters including ATP, opioids, and 5-HT. Right panel: 3) ATP activates P2Y autoreceptors. 4) Gβγ inhibits the Ca2+ channels, reducing Ca2+ entry and thereby exocytosis. 5) SERT mediated uptake of 5-HT opposes activation of the 5-HT1A receptors so this signaling pathway is not recruited. B) With sustained, stress-like stimulation 5-HT signaling becomes the dominant pathway for autocrine regulation. Left panel: 1-2) As in panel A, acetylcholine released from the splanchnic nerve depolarizes chromaffin cells opening voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and triggering exocytosis. 3) With sustained stimulation PACAP might also be released from the splanchnic nerve and become the main stress mediator activating the chromaffin cells. PACAP acts via PAC1 receptors which recruit additional Ca2+ entry pathways perhaps including CaV3 (T-type) channels and TRPC channels. Right panel: 4) ATP activates P2Y autoreceptors. 5) Inhibition of Ca2+ channels becomes ineffective with strong, sustained depolarization in part because Gβγ dissociates from the channels. 6) The stronger stimulation leads to greater increase in local 5-HT and activation of 5-HT1A receptors. 7) The 5-HT1A receptors inhibit exocytosis by an atypical mechanism independent from cellular excitability / Ca2+ entry that can persist during the sustained stimulation. In this manner, 5-HT signaling becomes the dominant pathway for autocrine regulation.