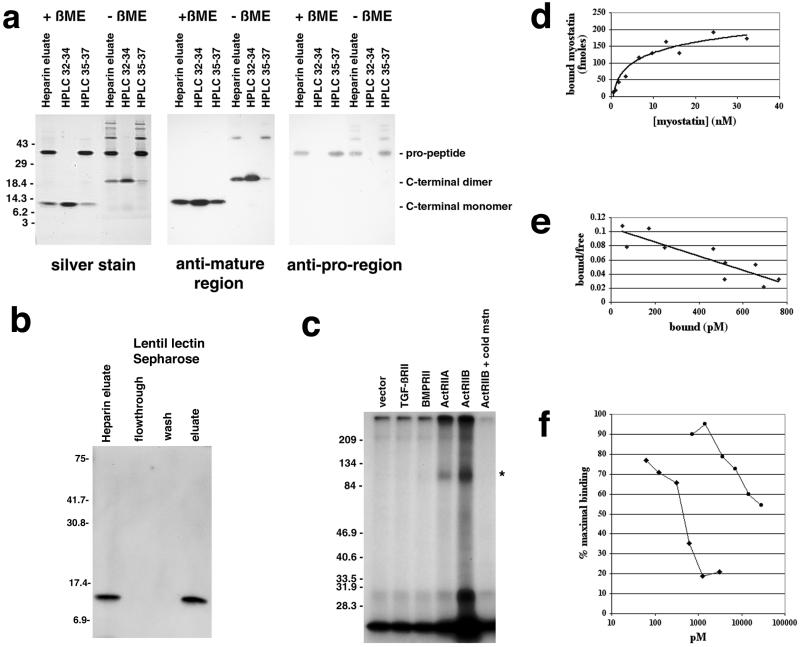
Figure 1.
Binding of myostatin to activin type II receptors. (a) Analysis of purified myostatin protein. Myostatin protein preparation following the heparin column (heparin eluate) or following reverse-phase HPLC (fractions 32–34 or 35–37 containing the C-terminal region or propeptide, respectively) was electrophoresed under reducing (+βME) or nonreducing (−βME) conditions and either silver stained or subjected to Western analysis. (b) Binding of myostatin to lentil lectin. The heparin eluate was bound to lentil lectin Sepharose and eluted with methyl mannose. Samples were electrophoresed under reducing conditions, blotted, and probed with antibodies directed against the C-terminal region. Similar analysis by using antibodies directed against the pro region showed that the pro region was also retained on the column and eluted with methyl mannose (data not shown). (c) Crosslinking experiments. COS-7 cells transfected with expression constructs for the indicated receptors were incubated with 125I-myostatin followed by the crosslinking agent disuccinimidyl suberate. Crosslinked complexes were analyzed by SDS/PAGE. Asterisk denotes predicted size for myostatin bound to an activin type II receptor. In the rightmost lane, excess unlabeled myostatin was included in the binding reaction. (d) Binding of myostatin to ActRIIB. All points represent the average of triplicate samples. (e) Scatchard analysis of the data shown in d. (f) Inhibition of myostatin binding to ActRIIB by follistatin (diamonds) and the propeptide (circles). Each experiment was carried out in triplicate, and each curve represents the average of three independent experiments.